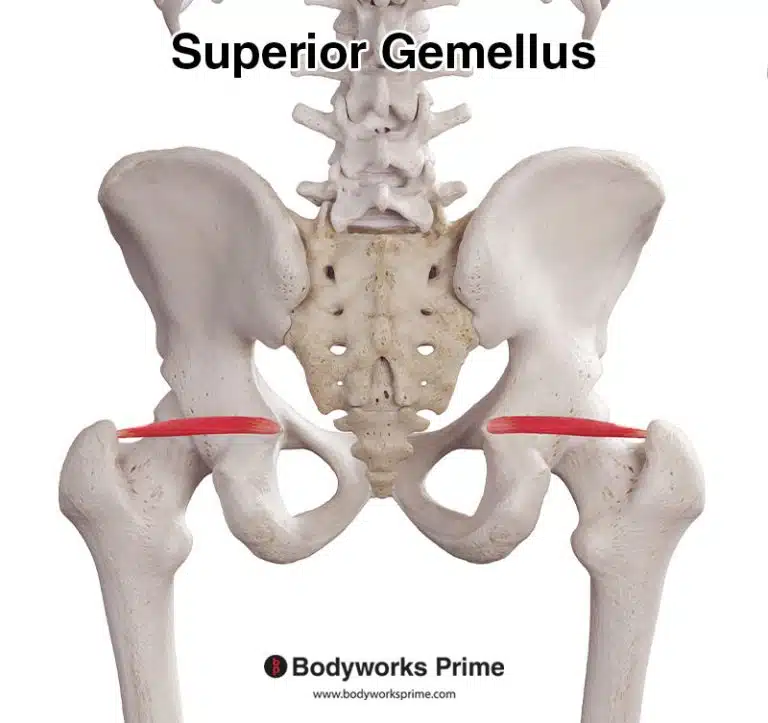
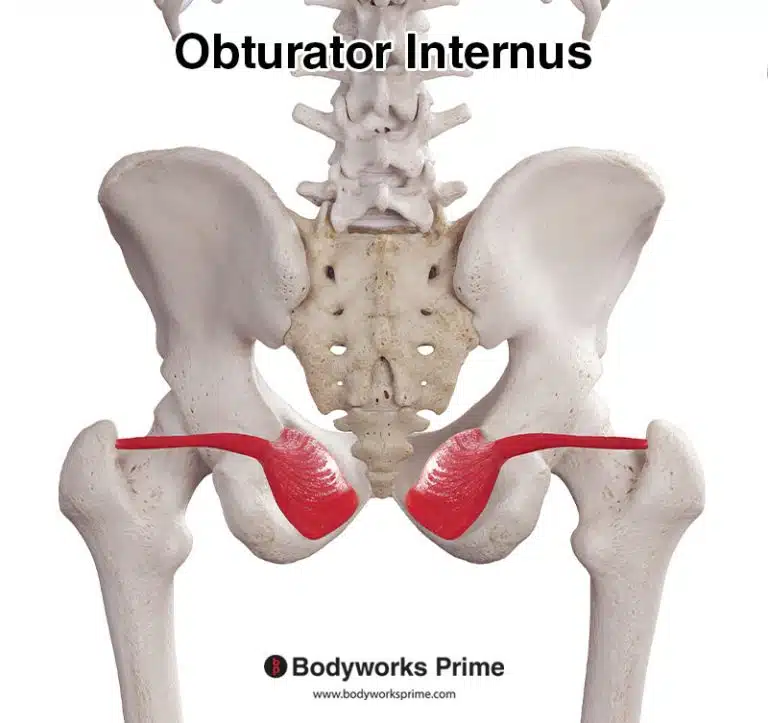
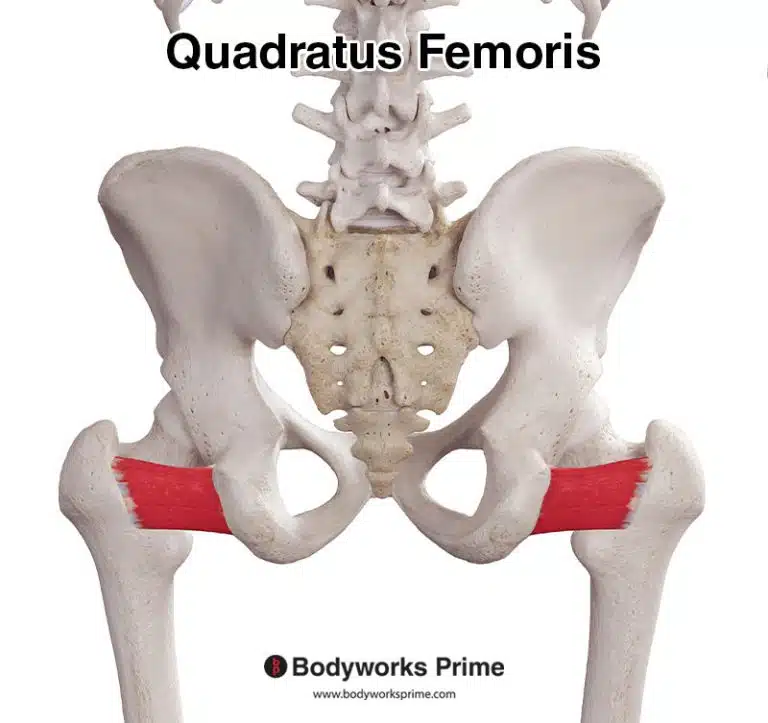
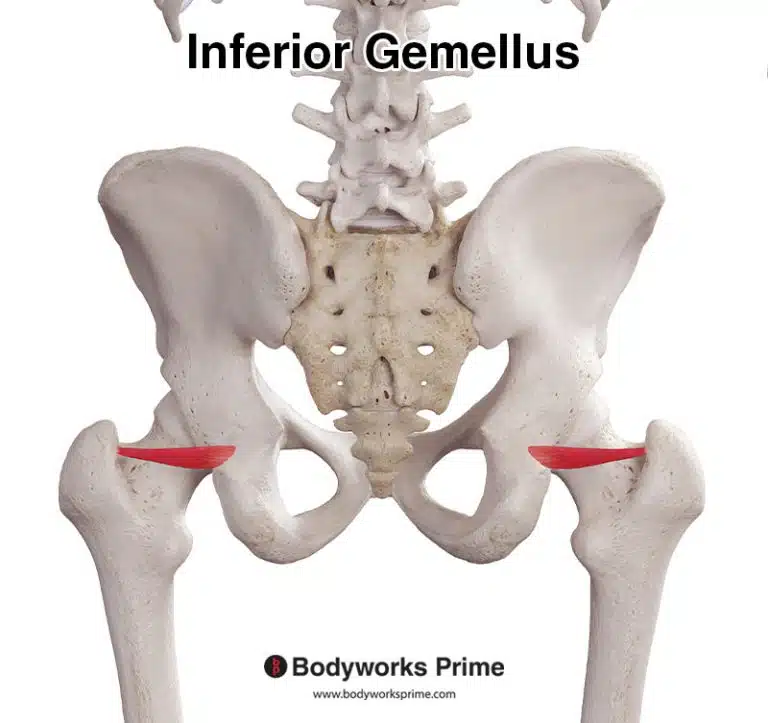
| Origin | Supraspinous fossa of scapula |
| Insertion | Greater tubercle of the humerus (superior aspect) |
| Action | Abduction of shoulder Weakly contributes to lateral rotation of the shoulder Stabilisation of the humerus in the glenohumeral joint |
| Nerve | Suprascapular nerve (C5, C6) |
| Artery | Suprascapular artery |
Location & Overview
The supraspinatus is a relatively small muscle which is located in the upper shoulder region. The supraspinatus muscle is one of the four rotator cuff muscles, which also include: the infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis muscles. A useful mnemonic to remember these muscles is “SITS” [1] [2].
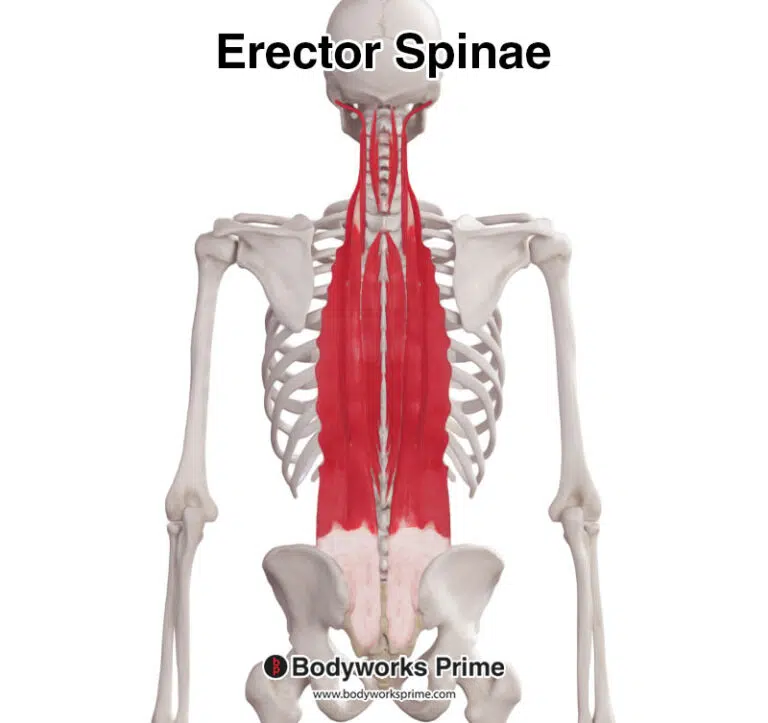
Occupying the supraspinous fossa of the scapula, above the spine of the scapula, the supraspinatus muscle is the most superiorly positioned rotator cuff muscle. The supraspinatus tendon extends laterally, passing beneath the acromion process and over the humerus’ head to insert onto the superior facet of the humerus’ greater tuberosity. Because the supraspinatus travels under the acromion, this can make it vulnerable to impingement. The space in this gap under the acromion is called the ‘subacromial space’. As part of the dynamic stabilisation system for the glenohumeral joint, the supraspinatus contributes significantly to shoulder stability and motion [3] [4] [5].
Common pathologies related to the supraspinatus muscle include rotator cuff tears, impingement syndromes, and tendinitis, which typically present as shoulder pain and restricted range of motion. Strengthening exercises, physical therapy, and surgical interventions are among the treatment options for these conditions [6] [7] [8].
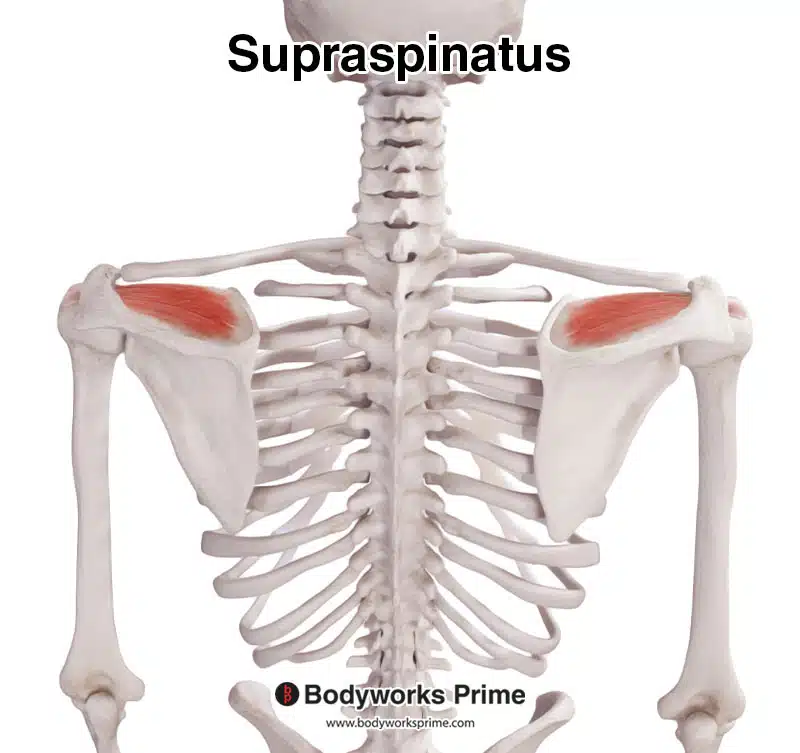
Here we can see the supraspinatus muscle, seen from a posterior view.
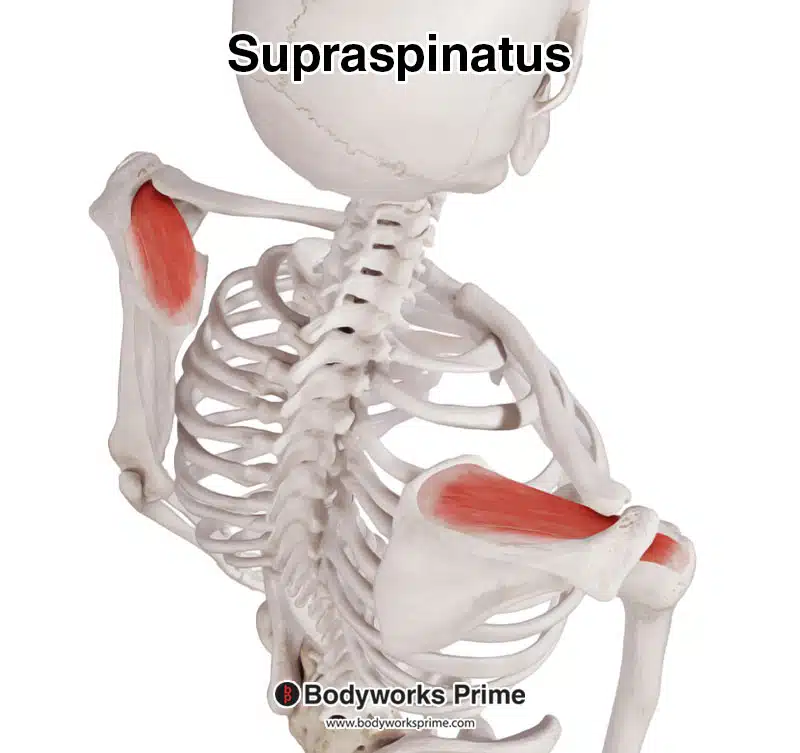
Here we can see the supraspinatus muscle, seen from a posterolateral and superior view.
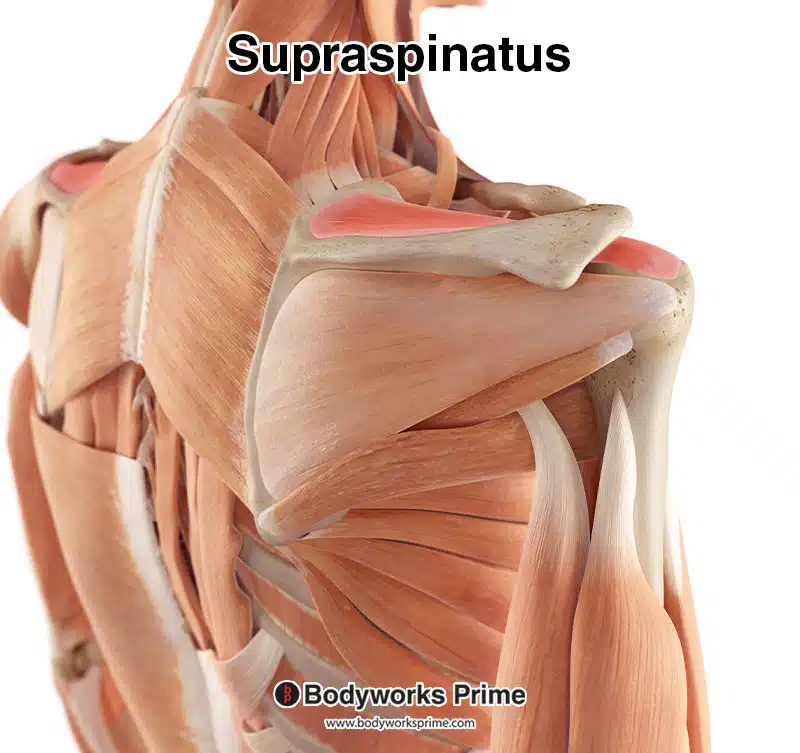
Here, the supraspinatus muscle is depicted among the other muscles of the body, highlighted in red. As the supraspinatus is a deep muscle, superficial muscles like the trapezius and deltoid have been removed for clarity, making the supraspinatus visible.
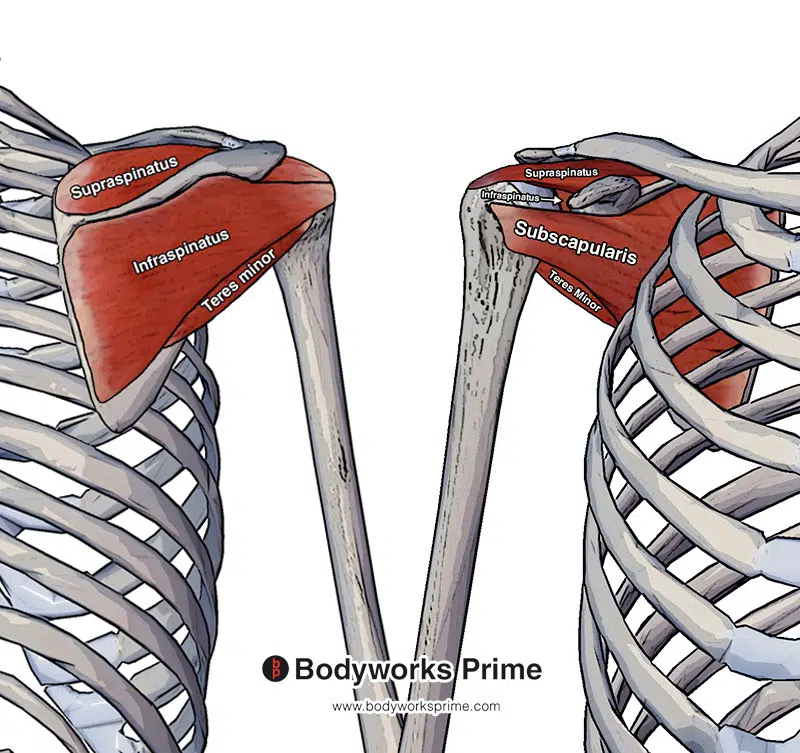
Pictured here we can see all four of the rotator cuff muscles: the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor and subscapularis. The left side of this picture is from a posterior view (the back) and the right hand side is from an anterior view (the front).
Origin & Insertion
The supraspinatus originates from the supraspinous fossa. The supraspinous fossa is a shallow depression found on the dorsal aspect of the scapula, located superior to the spine of the scapula. After originating here, its tendon extends laterally, passing underneath the acromion process. The acromion process is a bony extension of the scapula that forms the highest point of the shoulder on its lateral side [9] [10] [11] [12].
The insertion point of the supraspinatus muscle is the superior facet of the greater tuberosity of the humerus. The greater tuberosity is a large, bony prominence of the humerus, located on the lateral and proximal part of the bone. The superior facet refers to the topmost part of this bony landmark, where the supraspinatus tendon attaches [13] [14] [15] [16].
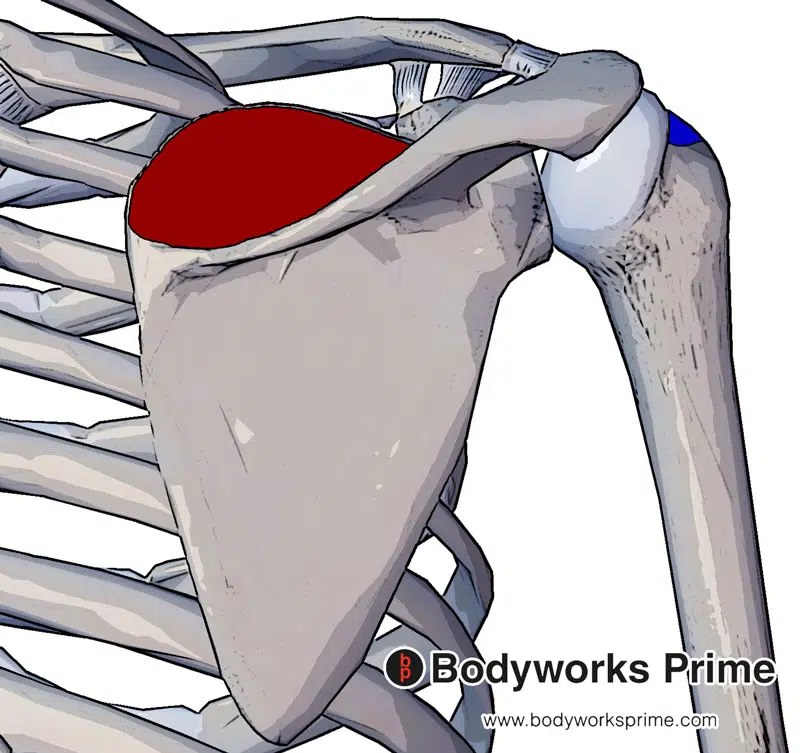
The supraspinatus originates at the supraspinous fossa of scapula (marked in red) and inserts at the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus (marked in blue).
Actions
The supraspinatus contributes to abduction of the humerus, allowing for movements such as lifting the arm to the side [17] [18] [19]. It also contributes weakly to the lateral (external) rotation of the humerus [20] [21] [22]. Furthermore, as part of the rotator cuff, the supraspinatus provides stability to the humerus’ head on the shallow glenoid fossa during joint movements and works with the deltoid muscle to prevent the downward displacement of the humeral head [23].
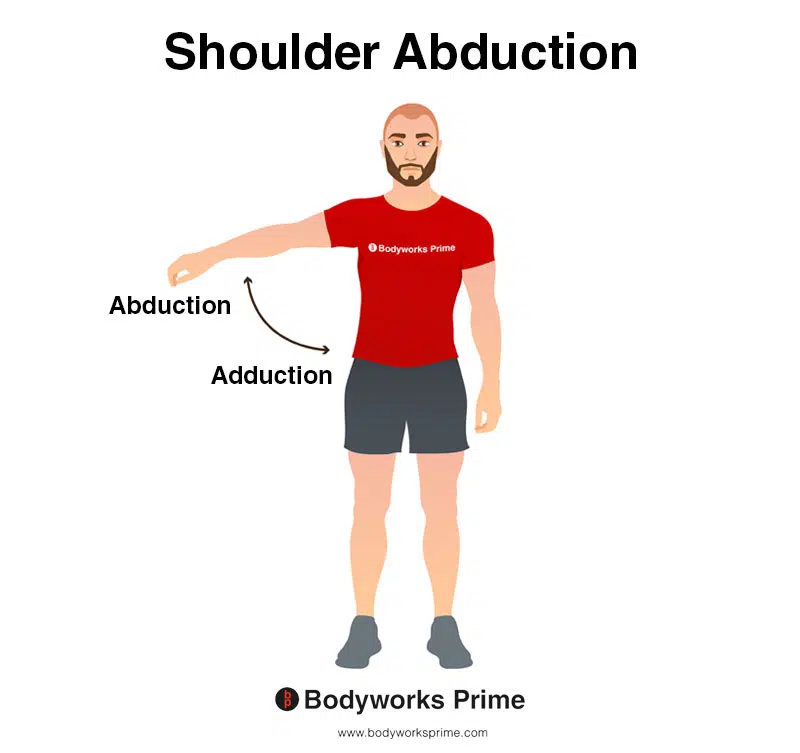
This image demonstrates shoulder abduction. Shoulder abduction involves lifting your arm out to the side of your body. The opposite of abduction is adduction, which involves bringing your arm back towards your body. The supraspinatus contributes to abduction of the humerus at the shoulder joint.
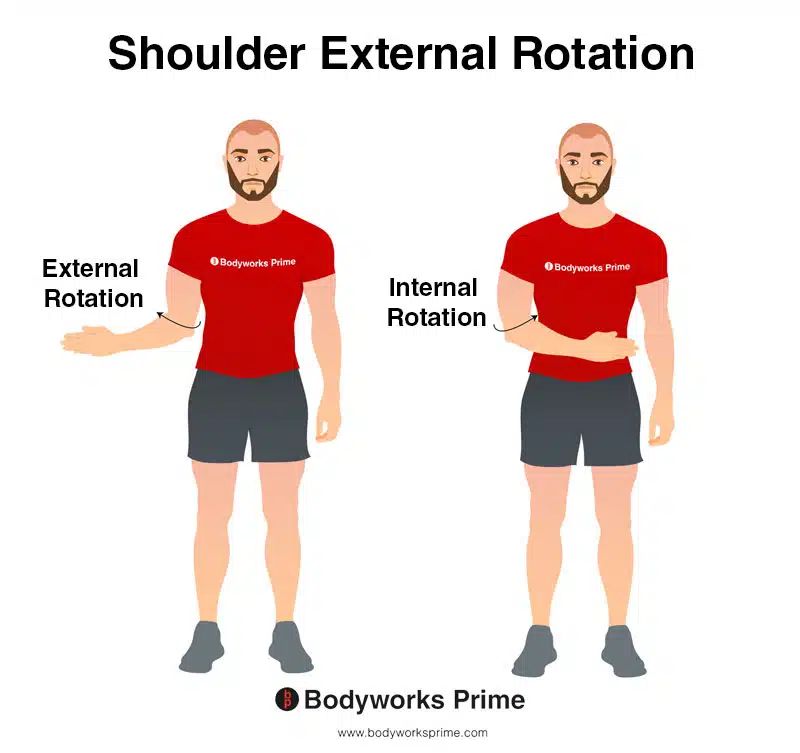
This image demonstrates the movement of external rotation of the shoulder. External rotation involves rotating your arm away from your body, towards the outside. In contrast, internal rotation involves rotating your arm towards the centre of your body, towards the inside. The supraspinatus contributes weakly to the lateral (external) rotation of the humerus at the shoulder joint.
Innervation
The supraspinatus is innervated by the suprascapular nerve, which originates from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus, from the nerve roots of C5 and C6. This nerve enables communication between the supraspinatus and the central nervous system. The suprascapular nerve also innervates the close by infraspinatus muscle [24] [25].
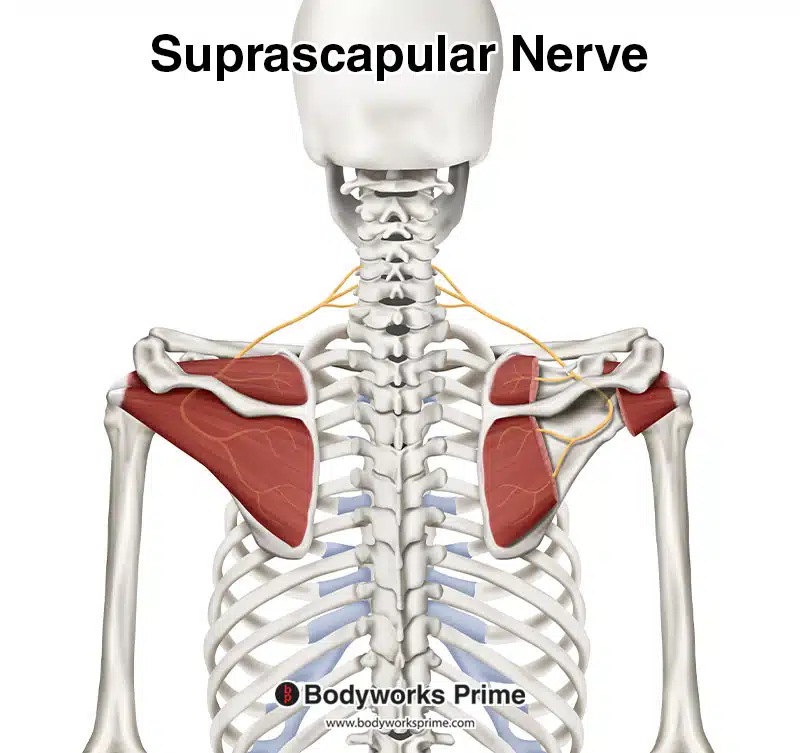
Here we can see the suprascapular nerve which innervates the supraspinatus muscle. This nerve originates from the nerve roots of C5 and C6.
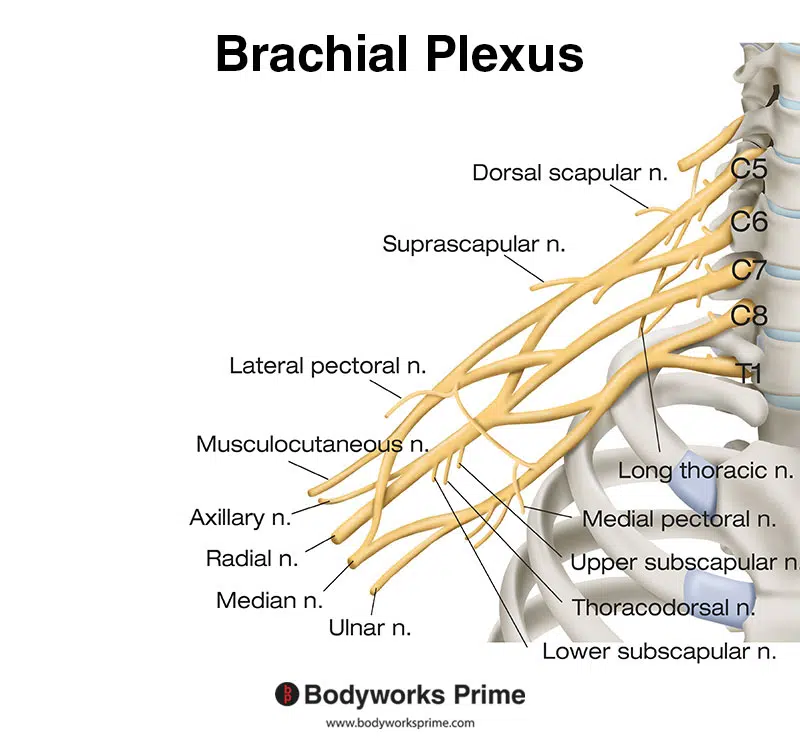
Here we can see the nerves of the brachial plexus. The suprascapular nerve is a part of the brachial plexus.
Blood Supply
The supraspinatus receives its blood supply mainly from the suprascapular and dorsal scapular arteries, which are branches of the thyrocervical trunk and the third part of the subclavian artery, respectively. These arteries provide the muscle with essential nutrients and oxygen for its optimal functioning [26] [27].
Want some flashcards to help you remember this information? Then click the link below:
Supraspinatus Flashcards
Support Bodyworks Prime
Running a website and YouTube channel can be expensive. Your donation helps support the creation of more content for my website and YouTube channel. All donation proceeds go towards covering expenses only. Every contribution, big or small, makes a difference!
References
| ↑1, ↑18, ↑25 | Standring S. (2015). Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 41st Edn. Amsterdam: Elsevier. |
|---|---|
| ↑2, ↑3, ↑6, ↑10, ↑14, ↑17, ↑24 | Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2017. |
| ↑4, ↑7, ↑11, ↑15 | Maruvada S, Madrazo-Ibarra A, Varacallo M. Anatomy, Rotator Cuff. [Updated 2023 Mar 27]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441844/ |
| ↑5, ↑8, ↑12, ↑16, ↑19, ↑22, ↑26 | Jeno SH, Munjal A, Schindler GS. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Arm Supraspinatus Muscle. [Updated 2022 Aug 30]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537202/ |
| ↑9, ↑13, ↑21 | Wu JG, Bordoni B. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Scapulohumeral Muscles. [Updated 2023 May 19]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546633/ |
| ↑20 | Langenderfer JE, Patthanacharoenphon C, Carpenter JE, Hughes RE. Variation in external rotation moment arms among subregions of supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and teres minor muscles. J Orthop Res. 2006 Aug;24(8):1737-44. doi: 10.1002/jor.20188. PMID: 16779813; PMCID: PMC1551907. |
| ↑23 | McCausland C, Sawyer E, Eovaldi BJ, et al. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Shoulder Muscles. [Updated 2022 Aug 8]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534836/ |
| ↑27 | de la Garza O, Lierse W, Steiner D. Anatomical study of the blood supply in the human shoulder region. Acta Anat (Basel). 1992;145(4):412-5. |