| Origin | Humeroulnar head: Medial epicondyle of humerus and coronoid process of ulna Radial head: Proximal half of anterior border of radius |
| Insertion | Bases of middle phalanges of digits two to five |
| Action | Flexion of fingers at proximal interphalangeal joints and at metacarpophalangeal joints Can also provide assistance during flexion of wrist |
| Nerve | Median nerve (C7, C8, T1) |
| Artery | Ulnar artery |
Location & Overview
The flexor digitorum superficialis is a forearm muscle that’s commonly considered a superficial muscle. This flexor digitorum superficialis crosses the elbow joint via the common flexor tendon, with the flexor digitorum profundus passing deep to it. The common flexor tendon is a band of fibrous connective tissue that attaches to the medial epicondyle of the humerus. The muscles that attach to the common flexor tendon include: the pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor digitorum superficialis, and the flexor carpi ulnaris. Distally, at the wrist, the flexor digitorum superficialis divides into four tendons. These four tendons travel deep to the flexor retinaculum via the carpal tunnel. The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway formed by the bones and ligaments of the wrist joint. The flexor retinaculum forms the anterior ‘roof’ of the carpal tunnel. When the flexor digitorum superficialis reaches the distal part of the proximal phalanx of the finger, an opening/split appears in the muscle tendon. This opening allows for the tendon of the flexor digitorum profundus muscle to pass through it [1] [2]. Images of this are included below.
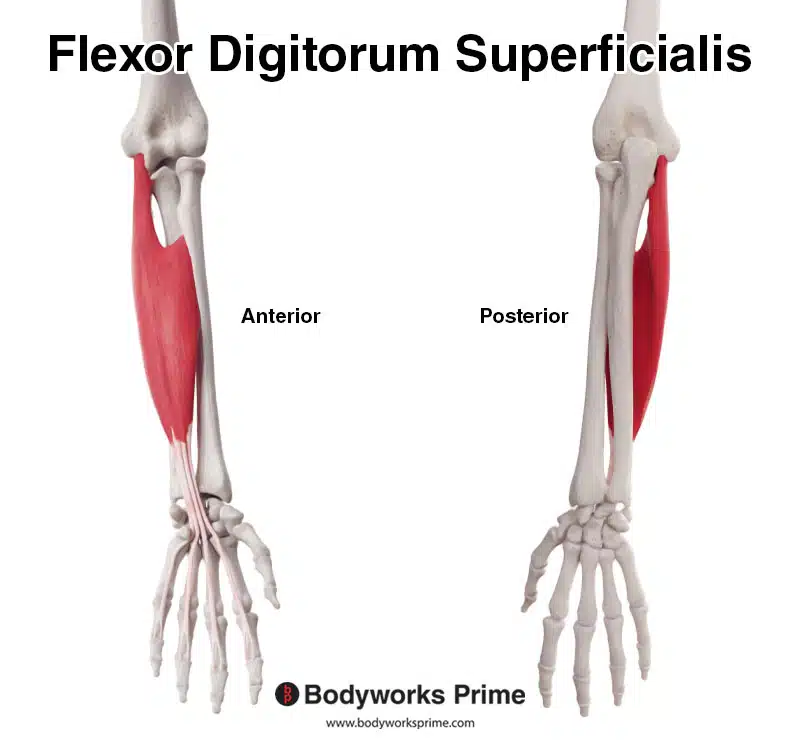
Here we can the flexor digitorum superficialis from a anterior and posterior view.
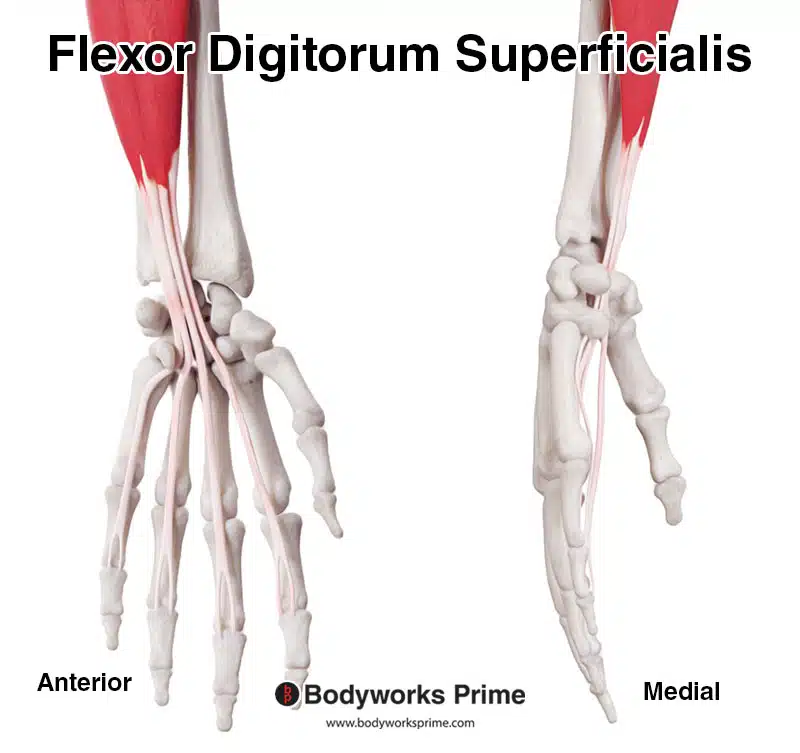
Here we can see a closer look at the distal tendon of the flexor digitorum superficialis.
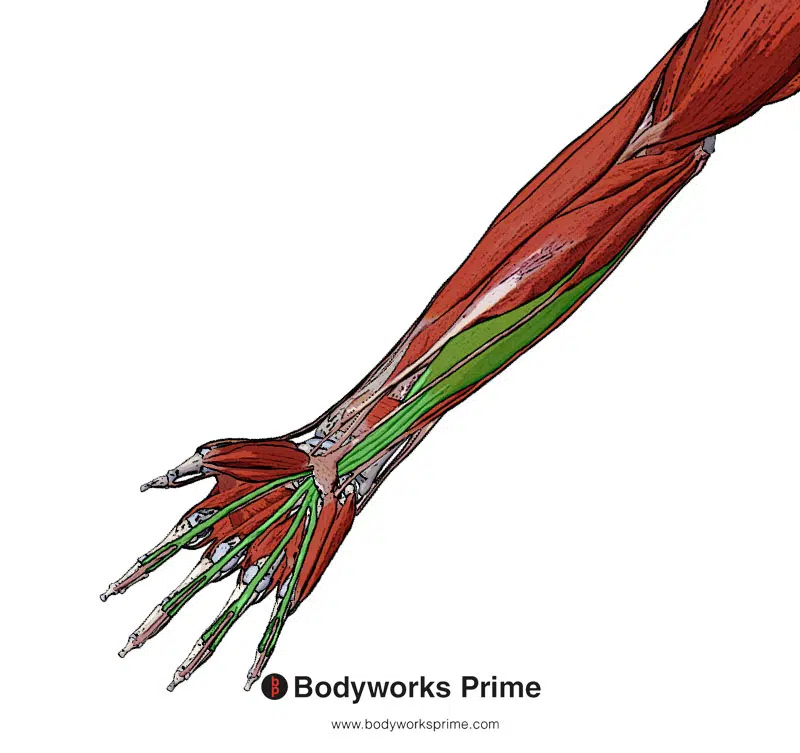
Highlighted in green, we can the flexor digitorum superficialis from a superficial view. You can see here how the flexor digitorum profundus passes through an opening in the superficialis at the most distal part of the tendon.
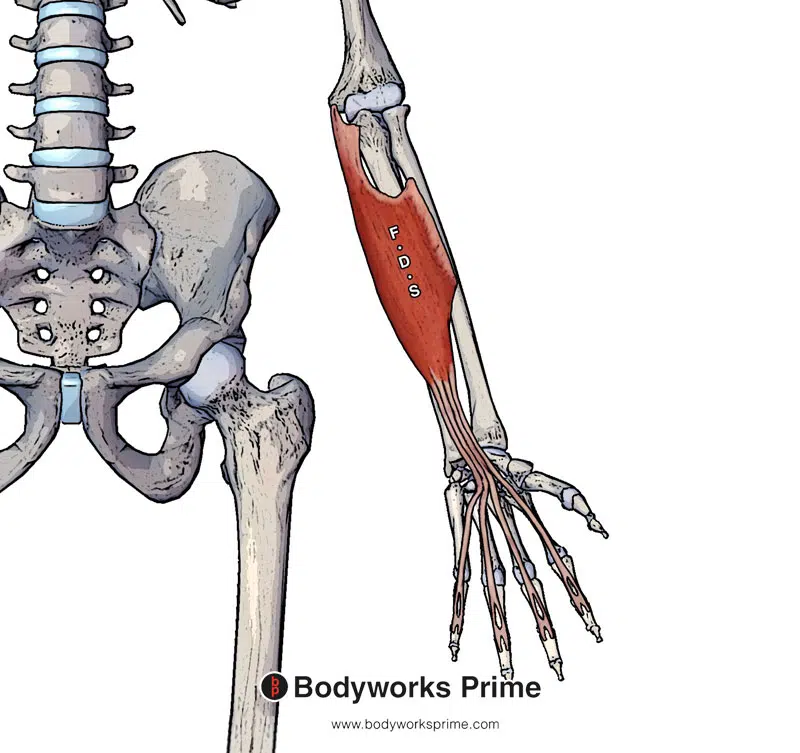
Here we can see the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle by itself.
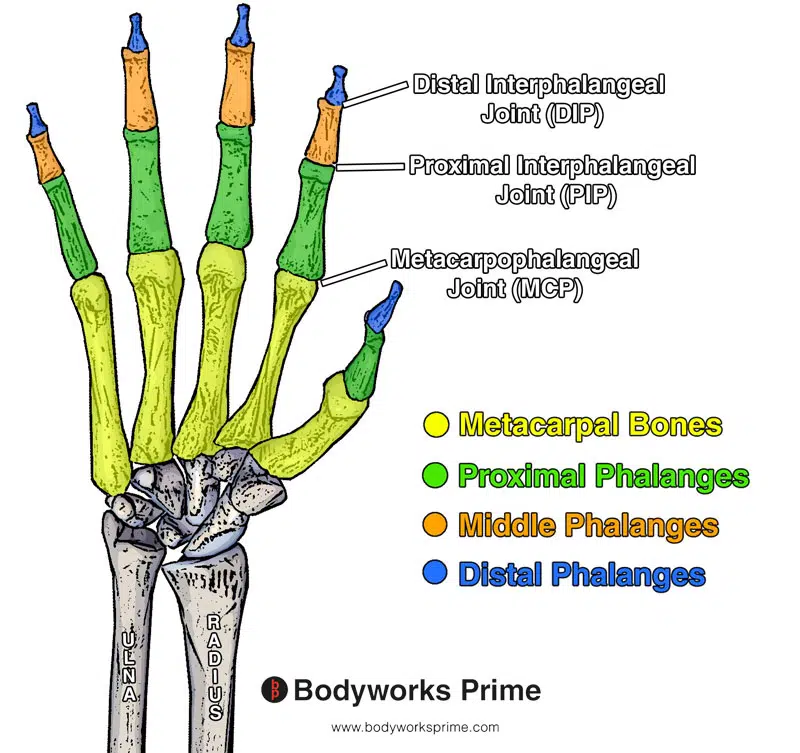
Here we can see a labelled diagram of the bones and the joints of the phalanges of the hand.
Origin & Insertion
There are two points of origin for the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle. The first is the humeroulnar head of the muscle, which originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and the coronoid process of the ulna. The second is the radial head, originating from the proximal half of the anterior border of the radius. The flexor digitorum superficialis then continues distally, where it crosses the wrist joint and reaches the fingers. It the inserts onto the bases of the middle phalanges of digits two to five [3] [4].
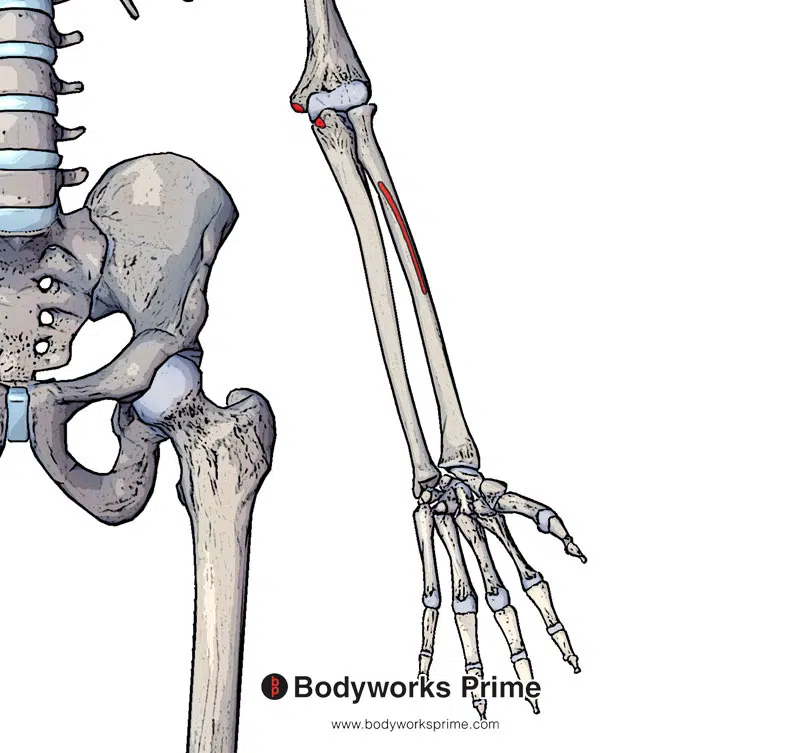
Here we can see the origin points of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle highlighted in red. The humeroulnar head originates on the medial epicondyle of humerus and coronoid process of the ulna. The radial head originates on the proximal half of the anterior border of the radius.
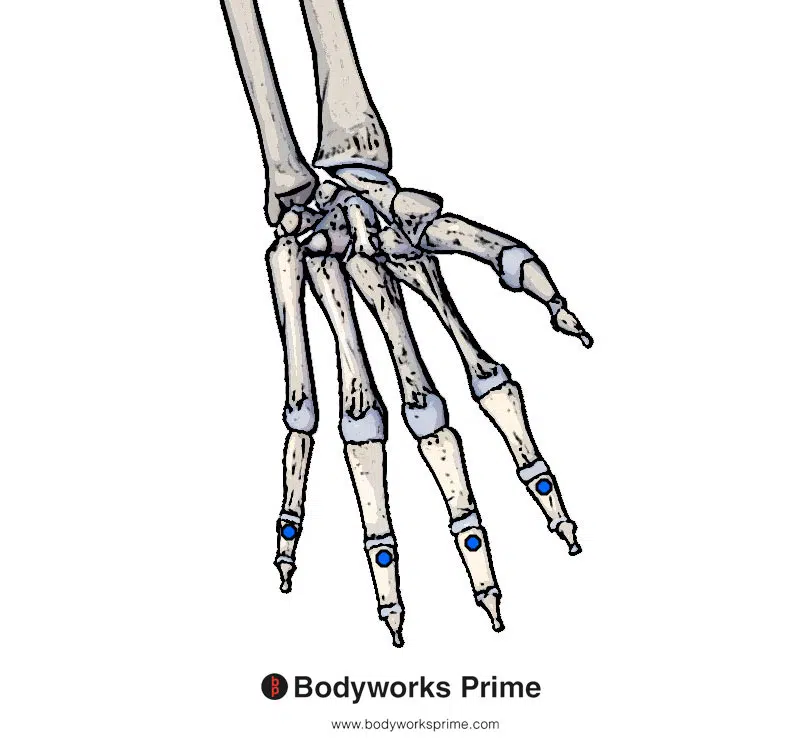
Here we can see the insertion points of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle highlighted in blue. The insertions are on the bases of the middle phalanges of digits two to five.
Actions
The flexor digitorum superficialis flexes the proximal interphalangeal joints and metacarpophalangeal joints of digits 2-5. It is also able to provide assistance during flexion of the wrist. The primary flexors of the wrist are the flexor carpi radialis and the flexor carpi ulnaris. The flexor digitorum superficialis is able to flex each of the fingers it connects to independently [5] [6].
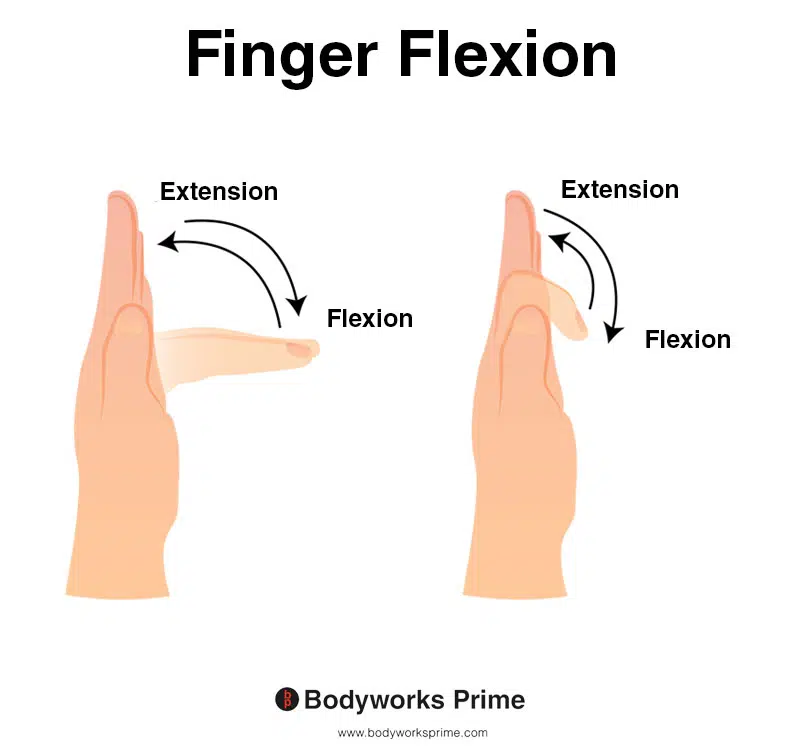
This image shows finger flexion, which involves bending the fingers towards the palm of the hand. On the left side of the image, we can see flexion occurring at the metacarpophalangeal joint, while on the right side, finger flexion occurs at the interphalangeal joints (specifically, the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints). However, it’s important to bear in mind that the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle only flexes the proximal interphalangeal joints and not the distal interphalangeal joints. Therefore, the joints located at the tips of the fingers won’t be flexed by the flexor digitorum superficialis.
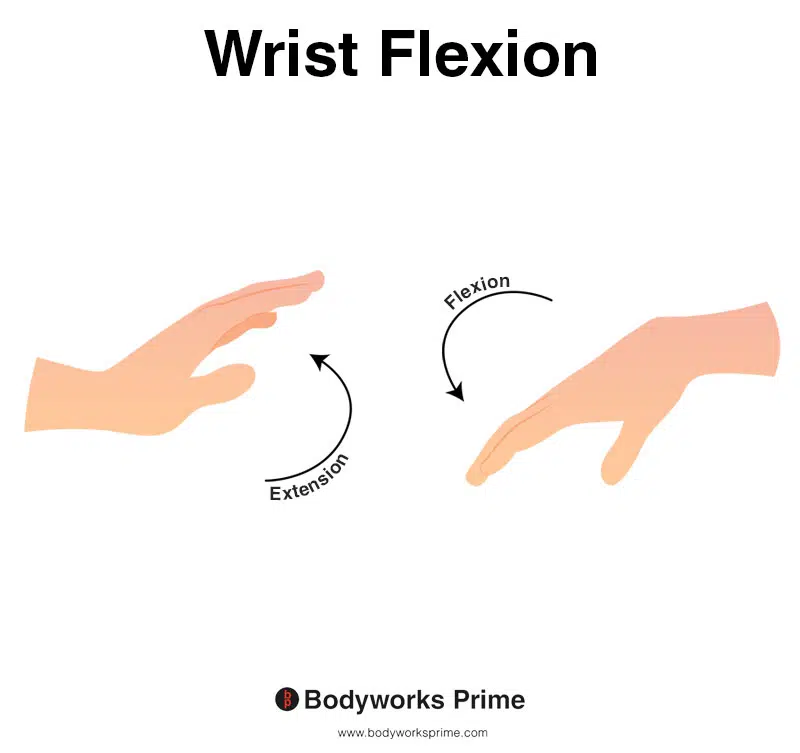
This image shows wrist flexion, which is the movement of bending the wrist in the direction of the underneath of the forearm (anterior surface of the forearm). The opposite of wrist flexion would be wrist extension which involves extending the wrist in the direction of the top of the forearm (posterior surface of the forearm). The flexor digitorum superficialis assists other muscles with flexion of the wrist.
Innervation
The median nerve and ulnar artery pass between the humeroulnar and radial heads of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle. The flexor digitorum superficialis muscle is innervated by the median nerve (C7, C8, T1) [7] [8].
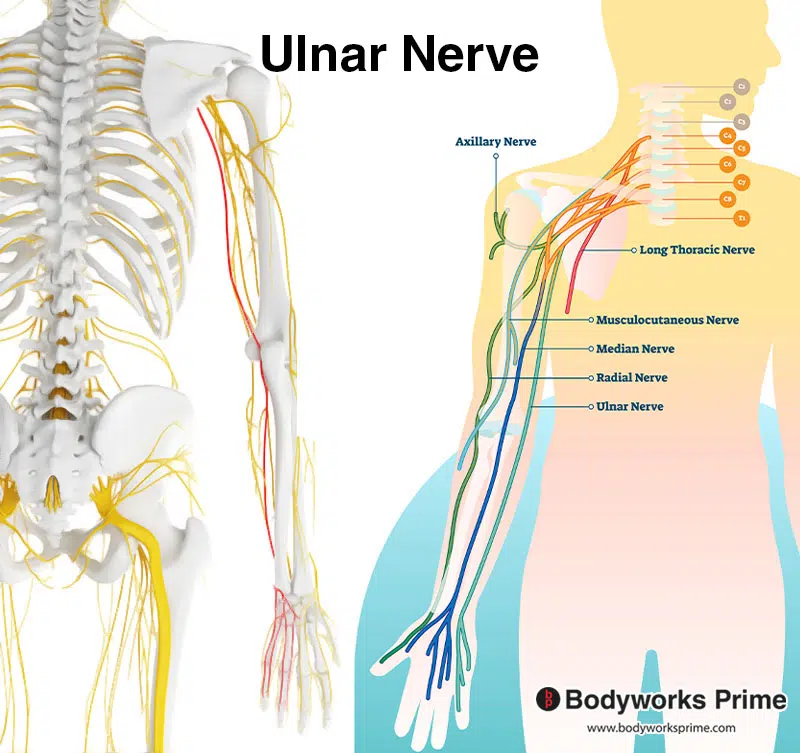
Pictured here we can see the ulnar nerve which innervates the flexor digitorum superficialis. The ulnar nerve is highlighted in red on the left of the picture.
Blood Supply
Blood is supplied to the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle primarily from the ulnar artery [9].
Want some flashcards to help you remember this information? Then click the link below:
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Flashcards
Support Bodyworks Prime
Running a website and YouTube channel can be expensive. Your donation helps support the creation of more content for my website and YouTube channel. All donation proceeds go towards covering expenses only. Every contribution, big or small, makes a difference!
References
| ↑1, ↑3, ↑5, ↑7, ↑9 | Okafor L, Varacallo M. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Flexor Digitorum Superficialis Muscle. [Updated 2021 Oct 21]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539723/ |
|---|---|
| ↑2, ↑4, ↑6, ↑8 | Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2017 |