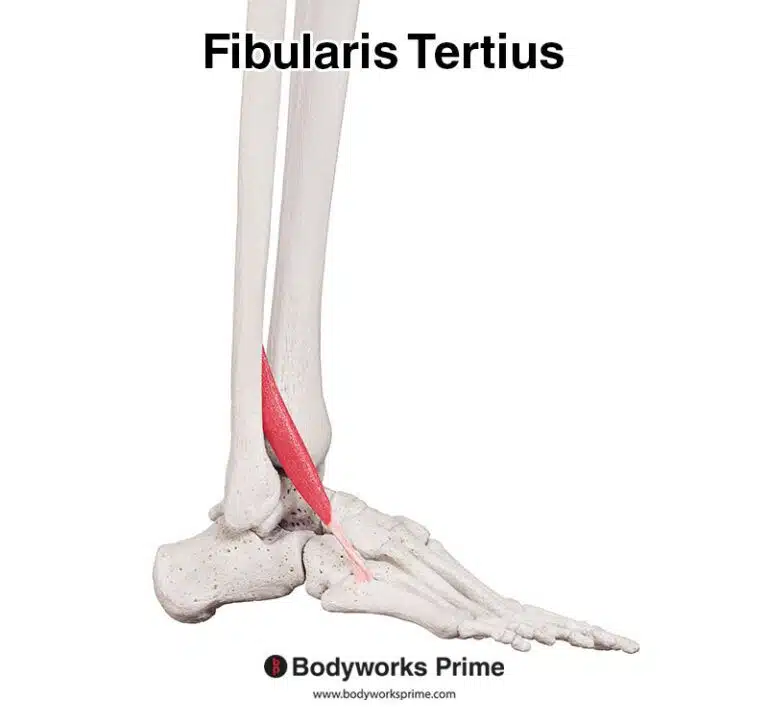
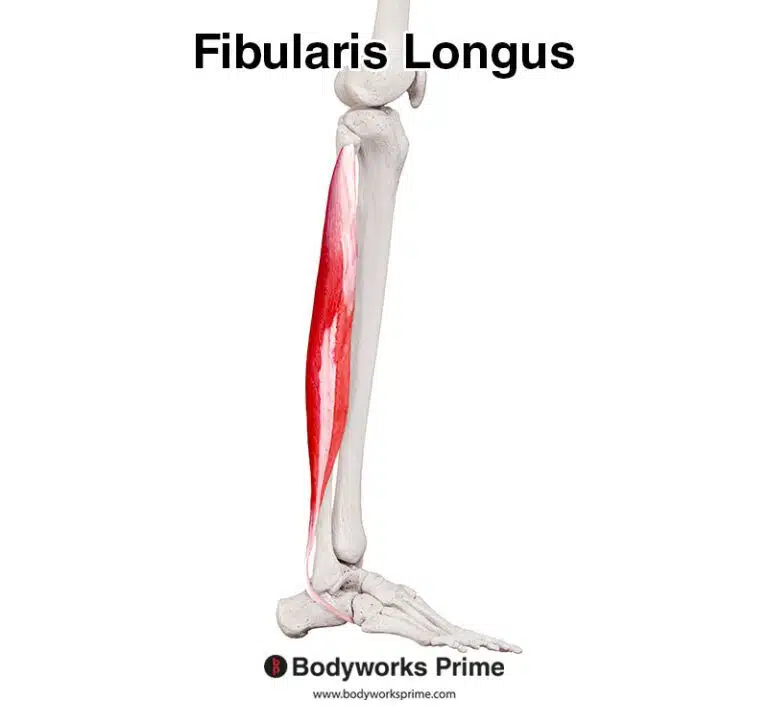
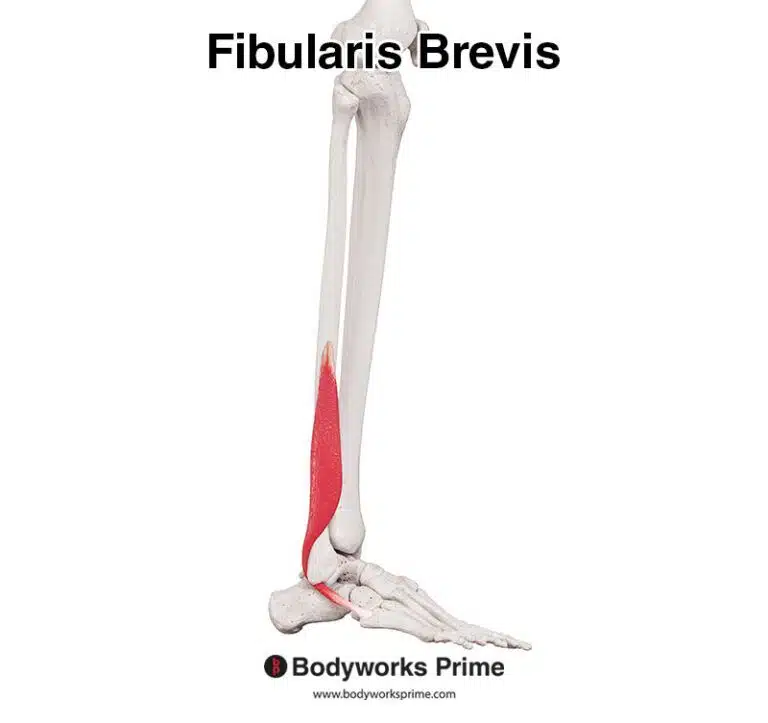
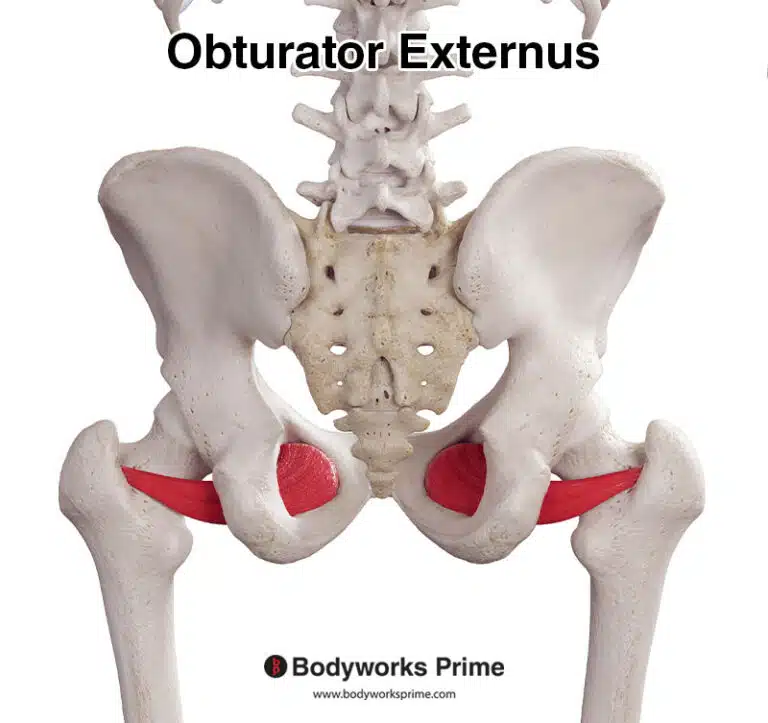
| Origin | Anterior surface radius Adjacent interosseous membrane of forearm |
| Insertion | Palmar aspect of base of distal phalanx of thumb |
| Action | Flexes thumb Very weakly assists in flexing the wrist |
| Nerve | Anterior interosseous nerve (C7, C8) |
| Artery | Anterior interosseous artery |
Location & Overview
The flexor pollicis longus muscle is located in the anterior part of the forearm and is one of the three deep flexor muscles found in the volar compartment of the forearm. The other two muscles in this compartment are the flexor digitorum profundus and pronator quadratus muscles. This muscle lies deep to the radial head of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle and is distal to the supinator muscle. Its primary function is to flex the thumb, making it a key muscle for grip strength. Despite being located in the forearm, the flexor pollicis longus is classified as one of the extrinsic muscles of the hand [1] [2] [3].
In Latin, ‘pollicis’ means ‘of the thumb’, ‘flexor’ means ‘a muscle that flexes a joint’, and ‘longus’ means ‘long’. So translated into English, flexor pollicis longus is ‘long flexor muscle of the thumb’. Studies have shown that the flexor pollicis longus is only present in approximately 48% of the population [4].
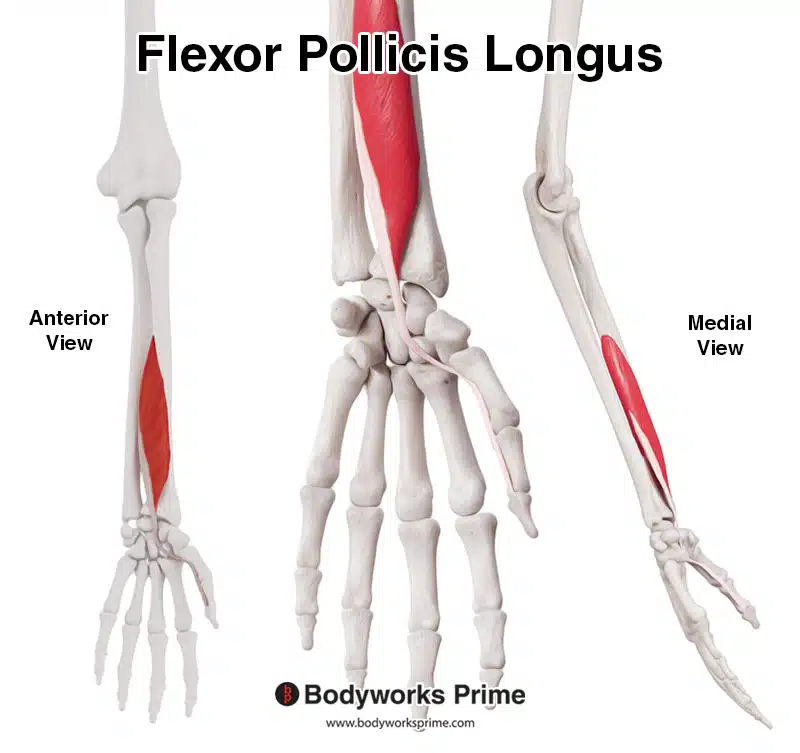
Here we can see the flexor pollicis longus muscle from multiple views.
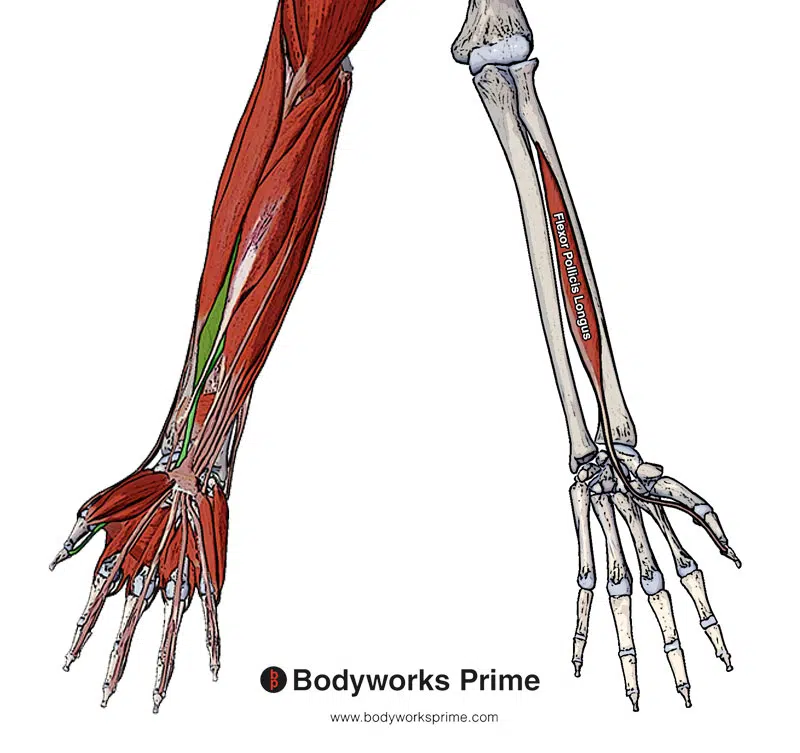
Here we can see the flexor pollicis longus muscle. We can see a superficial view with the flexor pollicis longus highlighted in green and an isolated view of the muscle by itself.
Origin & Insertion
The flexor pollicis longus originates on the anterior surface of the radius (also know as the volar aspect), just distal to the radial tuberosity. It also originates from the adjacent interosseous membrane. The interosseous membrane is a strong fibrous sheet that connects the radius and ulna bones, which run parallel to each other in the forearm. The flexor pollicis longus also passes deep to the flexor retinaculum, also known as the transverse carpal ligament. The muscle then proceeds towards its insertion on the palmar aspect of the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb [5] [6] [7].
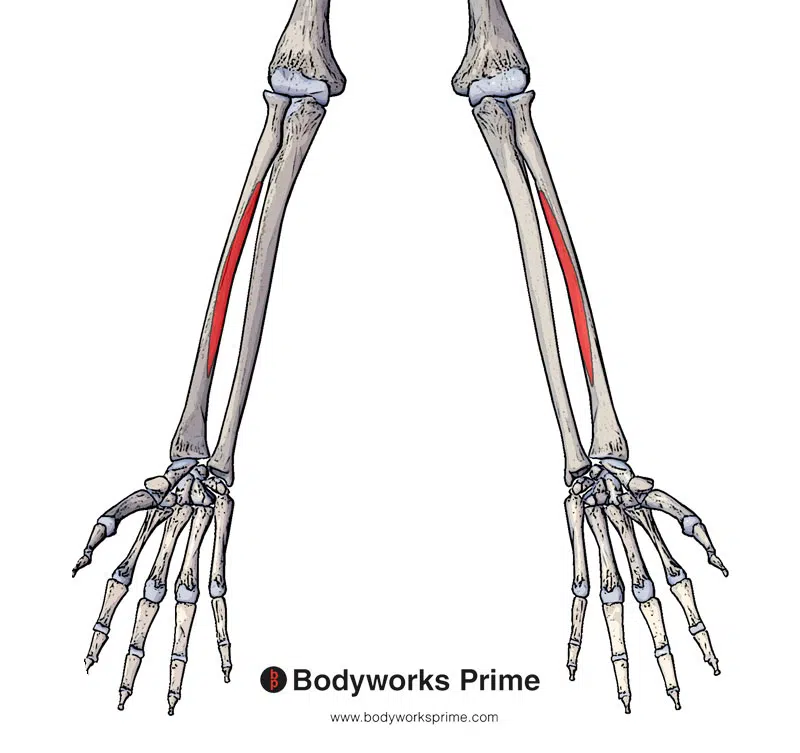
Here we can see the first origin point of the flexor pollicis longus highlighted in red. The origin is on the anterior surface of the radius.
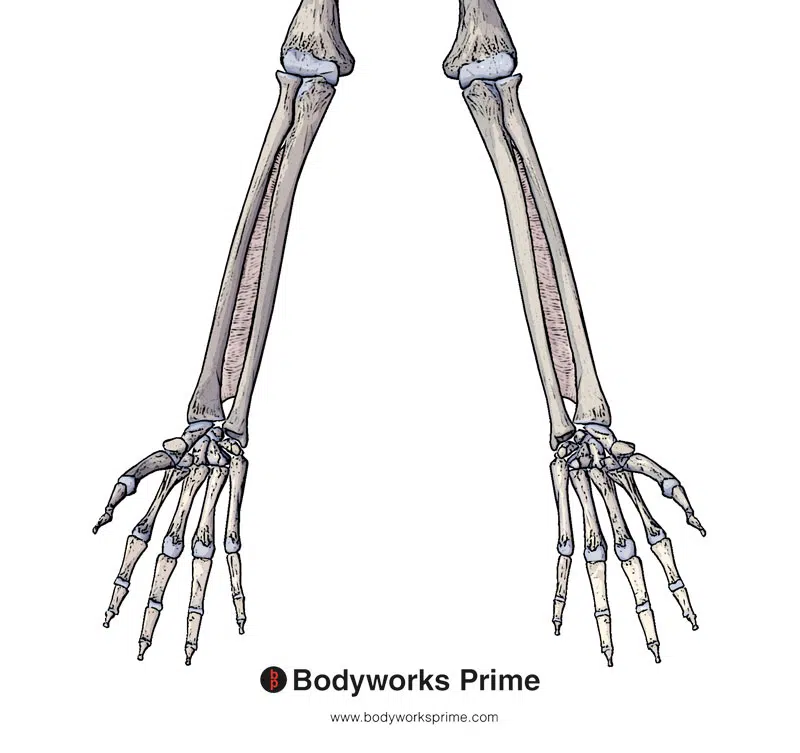
Here we can see the interosseous membrane of forearm which is an origin of the flexor pollicis longus.
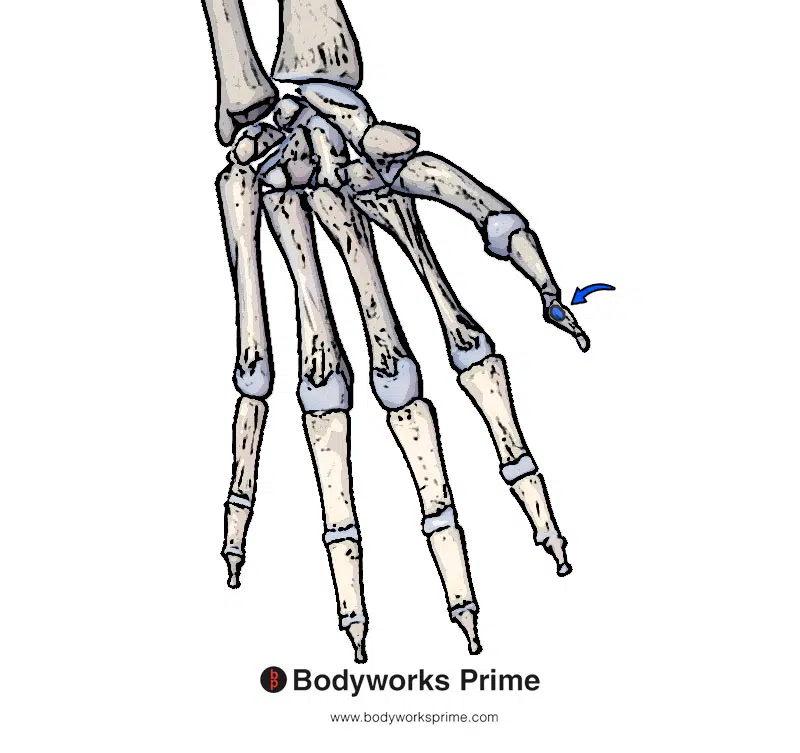
Here we can see the insertion of the flexor pollicis longus highlighted in blue. The insertion is on the palmar aspect of the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb.
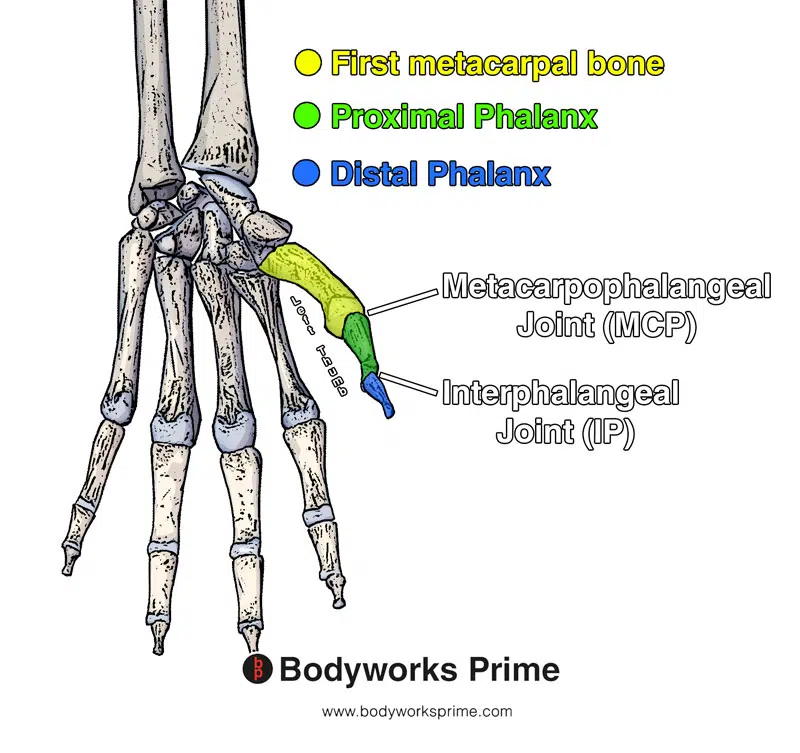
Here we can see the different bones and joints in the thumb colour coded to their respective location.
Actions
The flexor pollicis longus muscle is the primary flexor of the thumb. It provides flexion at both the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints. In addition to thumb flexion, it can support other muscles by contributing weak flexion of the wrist joint [8] [9].
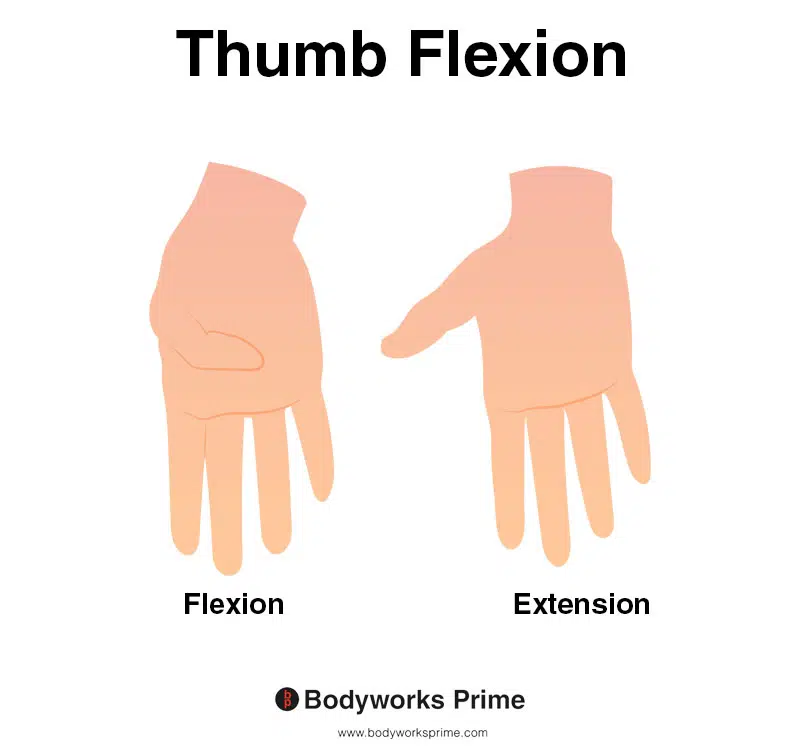
This image demonstrates thumb flexion, which is the action of bending the thumb inwards towards the palm of the hand. The left side of the image depicts thumb flexion, while the right side shows thumb extension. Thumb extension is the opposite action to thumb flexion. The flexor pollicis longus muscle is the primary flexor of the thumb.
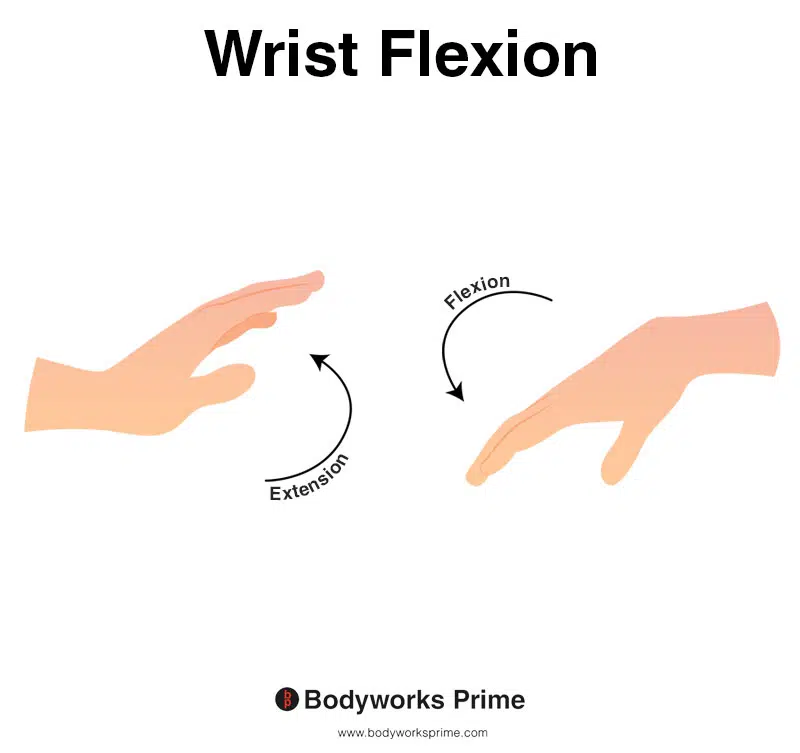
This image shows wrist flexion, which is the movement of bending the wrist in the direction of the underneath of the forearm (anterior surface of the forearm). The opposite of wrist flexion would be wrist extension which involves extending the wrist in the direction of the top of the forearm (posterior surface of the forearm). The flexor pollicis longus is able to contribute weakly to flexion of the wrist joint.
Innervation
The flexor pollicis longus is innervated by the anterior interosseous nerve. The anterior interosseous nerve is a branch of the median nerve and passes in between the two heads of the pronator teres muscle [10] [11].
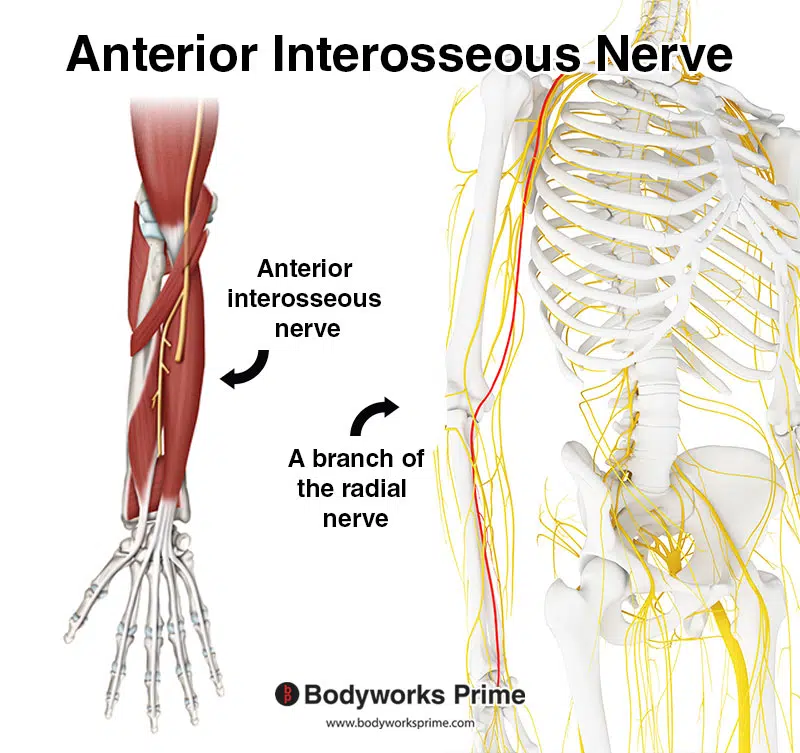
Pictrured here we can see the anterior interosseous nerve which is a branch of the radial nerve. The radial nerve is highlighted in red on the right hand side.
Blood Supply
Blood is supplied to the flexor pollicis longus from the anterior interosseous artery. The anterior interosseous artery is a branch of the ulnar artery. Branches of the median nerve artery also provide blood to the flexor pollicis longus’ pre-digital portion. The digital portion of the tendon gets its blood supply from vincula: V1 and V2. V1 originates from either the princeps pollicis artery or both digital arteries. V2 originates from both digital arteries [12] [13].
Want some flashcards to help you remember this information? Then click the link below:
Flexor Pollicis Longus Flashcards
Support Bodyworks Prime
Running a website and YouTube channel can be expensive. Your donation helps support the creation of more content for my website and YouTube channel. All donation proceeds go towards covering expenses only. Every contribution, big or small, makes a difference!
References
| ↑1, ↑5, ↑8, ↑10, ↑12 | Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2017 |
|---|---|
| ↑2, ↑6, ↑9, ↑11, ↑13 | Benson DC, Miao KH, Varacallo M. Anatomy, Shoulder and Upper Limb, Hand Flexor Pollicis Longus Muscle. [Updated 2021 Jul 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538490/ |
| ↑3, ↑7 | Standring S. (2015). Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 41st Edn. Amsterdam: Elsevier. |
| ↑4 | Asghar, A., Jha, R. K., Patra, A., Chaudhary, B., & Singh, B. (2022). The prevalence and distribution of the variants of Gantzer’s muscle: a meta-analysis of cadaveric studies. Anat Cell Biol, 55(1), 3-13. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.21.141 |