| Origin | Thoracolumbar fascia Iliac crest Inguinal ligament |
| Insertion | Inferior margins of tenth to twelfth ribs and adjacent costal cartilages Linea alba Pectineal line of the pubis (pecten pubis) |
| Action | Lateral flexion of the torso (unilateral contraction) Rotation of the torso (unilateral contraction) Flexion of the torso (bilateral contraction) Can assist in increasing intraabdominal pressure |
| Nerve | Anterior rami of intercostal nerves (T7-T11) Subcostal nerve (T12) Iliohypogastric nerve (L1) Ilioinguinal nerve (L1) |
| Artery | Lower posterior intercostal arteries and subcostal arteries Superior and inferior epigastric arteries Superficial and deep circumflex arteries Posterior lumbar arteries |
Location & Overview
The internal oblique muscle is located deep to the external oblique muscle and superficial to the transversus abdominis muscle (i.e located between these two muscle). Its fibers are obliquely oriented hence the name. The internal oblique is much thinner and smaller than the external oblique and much like the external oblique it is a flat and sheet like shape which wraps around the abdomen. The internal oblique is one if the five abdominal muscles. The other four are: the external oblique, rectus abdominis, transversus abdominis and the pyramidalis [1] [2] [3].
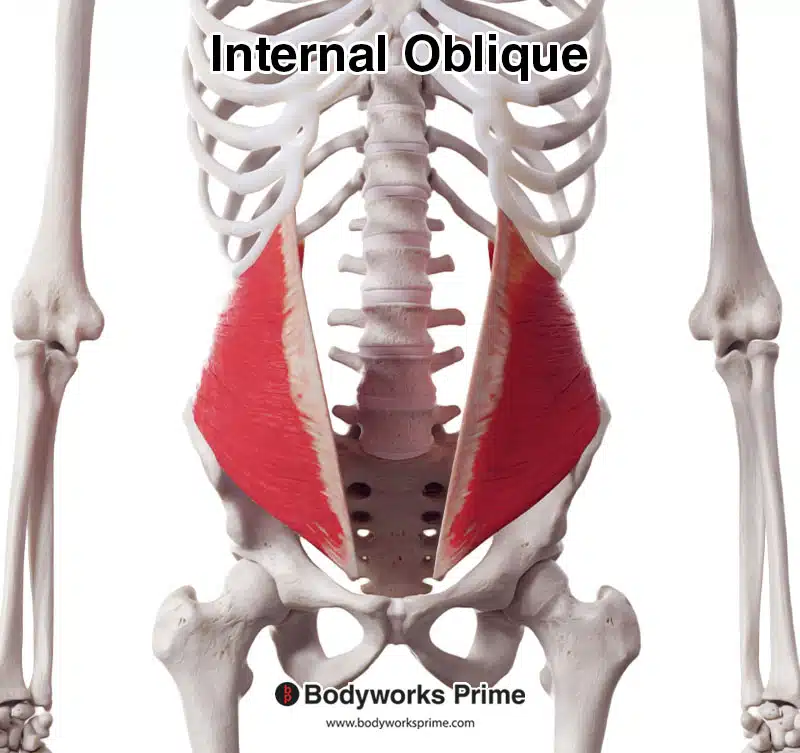
Here we can see the internal oblique from an anterior view.
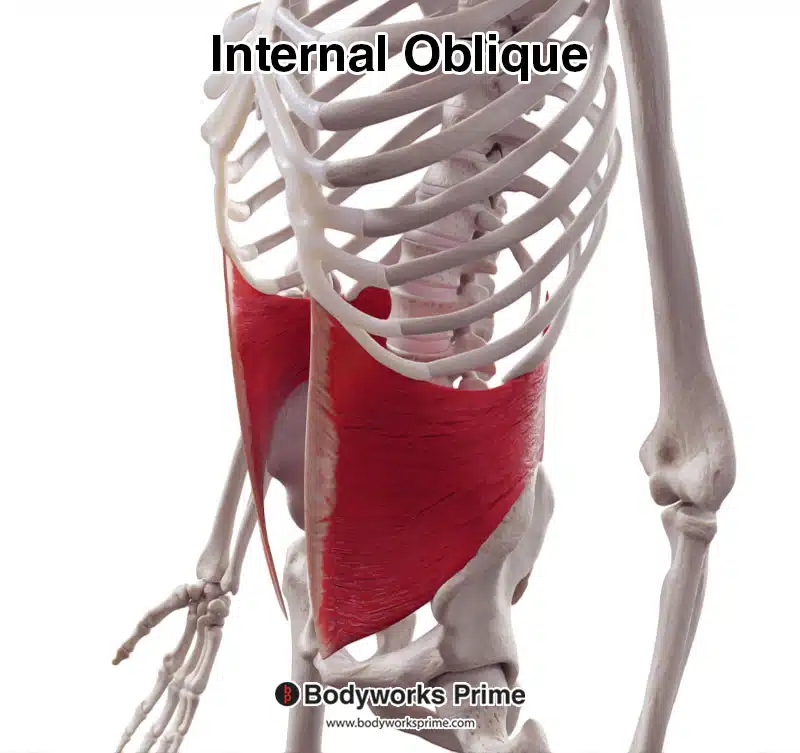
Here we can see the internal oblique from an anterolateral view.
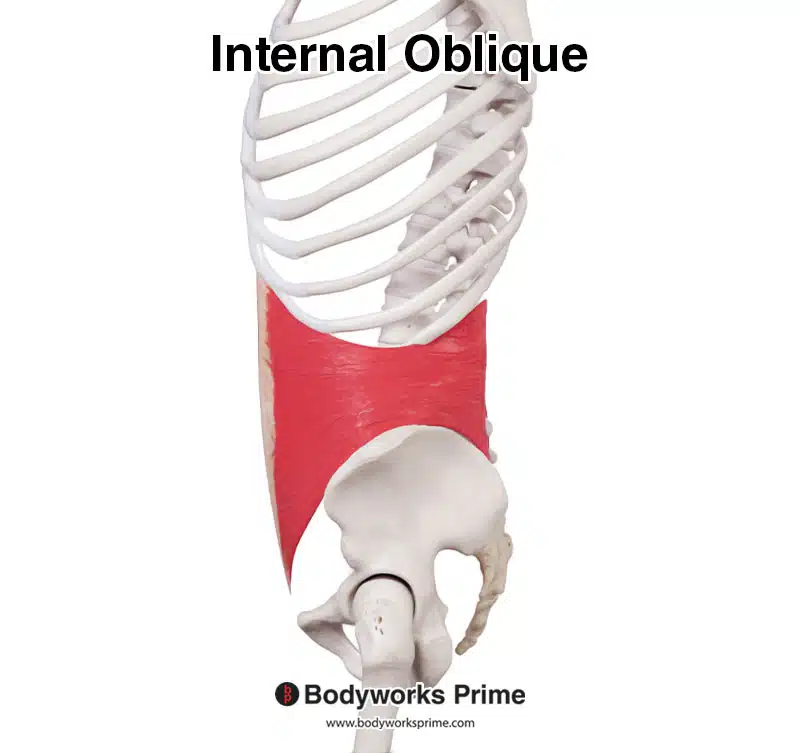
Here we can see the internal oblique from a lateral view.
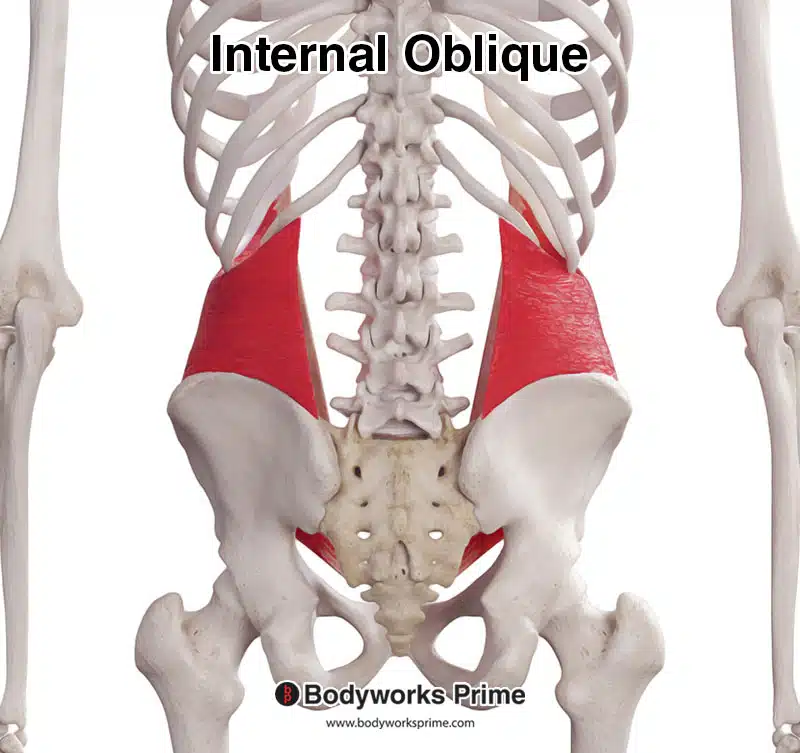
Here we can see the internal oblique from a posterior view.
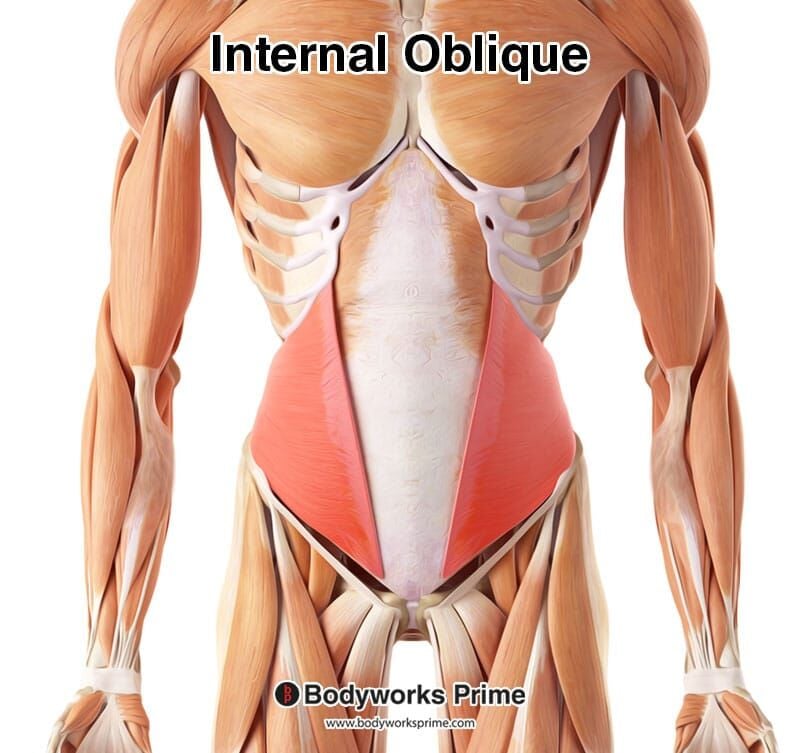
Here we can see the internal oblique highlighted in red amongst the other muscles of the body. Due to the internal oblique being a somewhat deep muscle, more superficial muscles like the rectus abdominis and the external oblique have been removed to fully reveal the internal oblique. The muscle underlying the internal oblique here is the transversus abdominis.
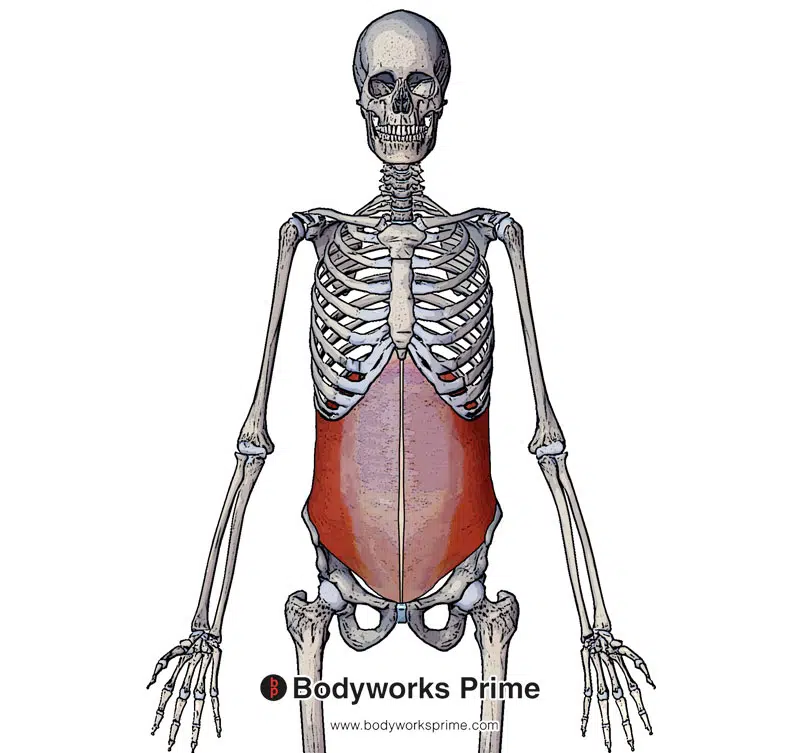
Pictured here we can the internal oblique muscle with its aponeurosis connecting into the linea alba at the midline.
Origin & Insertion
The internal oblique originates from the thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, and the lateral two thirds of the inguinal ligament. Its fibers run in a superomedial direction and as they near the midline, they form an aponeurosis. This aponeurosis then inserts at the linea alba. The superior aspect of the internal oblique inserts onto the inferior borders of the tenth to twelfth ribs. Inferiorly the internal oblique inserts at the pectineal line of the pubis (also known as the pectin pubis) [4] [5] [6].
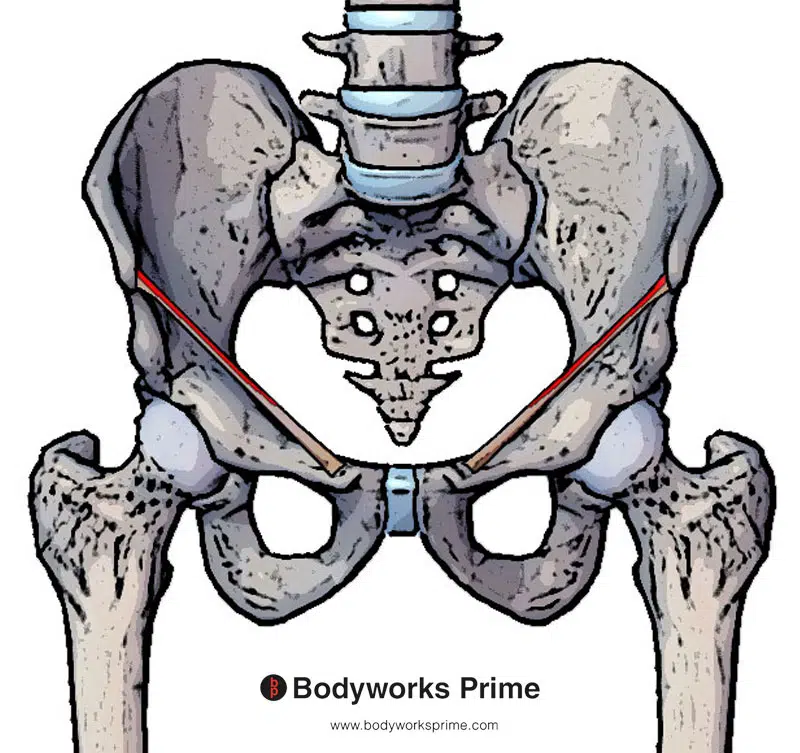
Pictured here we can see an origin of the internal oblique muscle on the lateral two thirds of the inguinal ligament (highlighted in red).
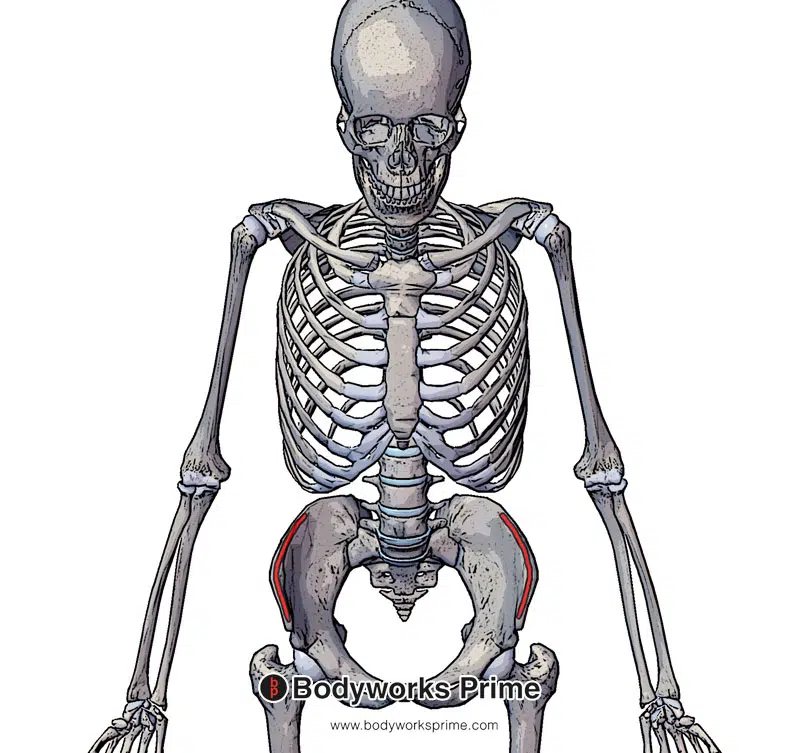
Pictured here we can see an origin of the internal oblique muscle on the iliac crest (highlighted in red).
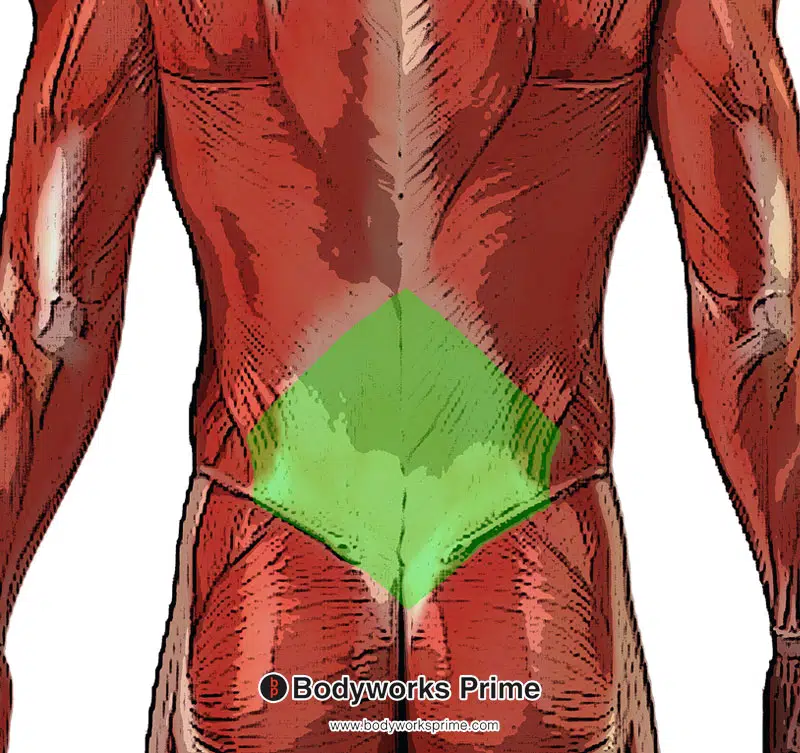
Pictured here we can see an origin of the internal oblique muscle on the thoracolumbar fascia (highlighted in green).
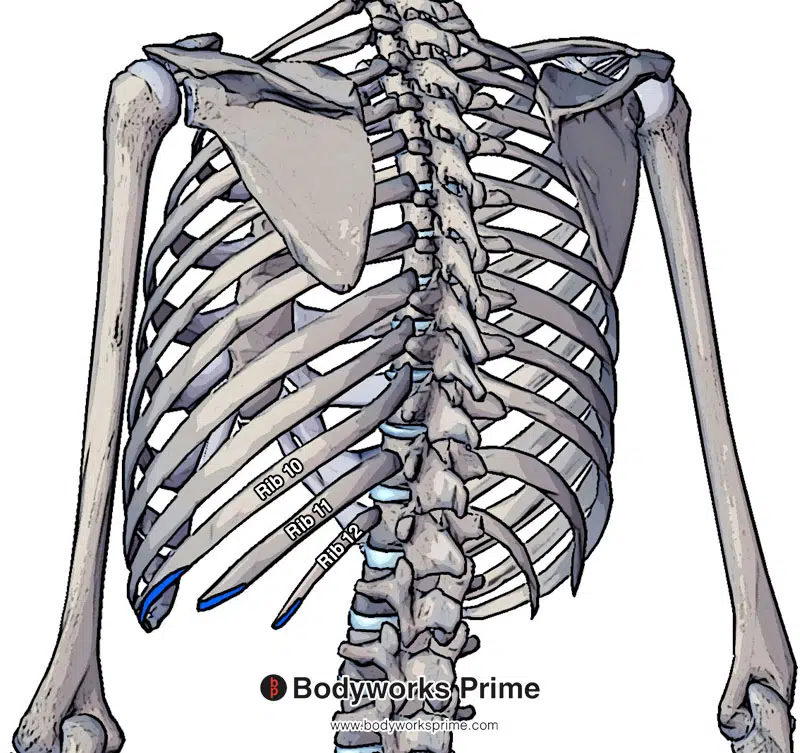
Pictured here we can see an insertion of the internal oblique muscle on the inferior margins of tenth to twelfth rib (highlighted in blue). This is from a posterior view, from an anterior view we will be able to see it connecting onto the adjacent costal cartilages also.
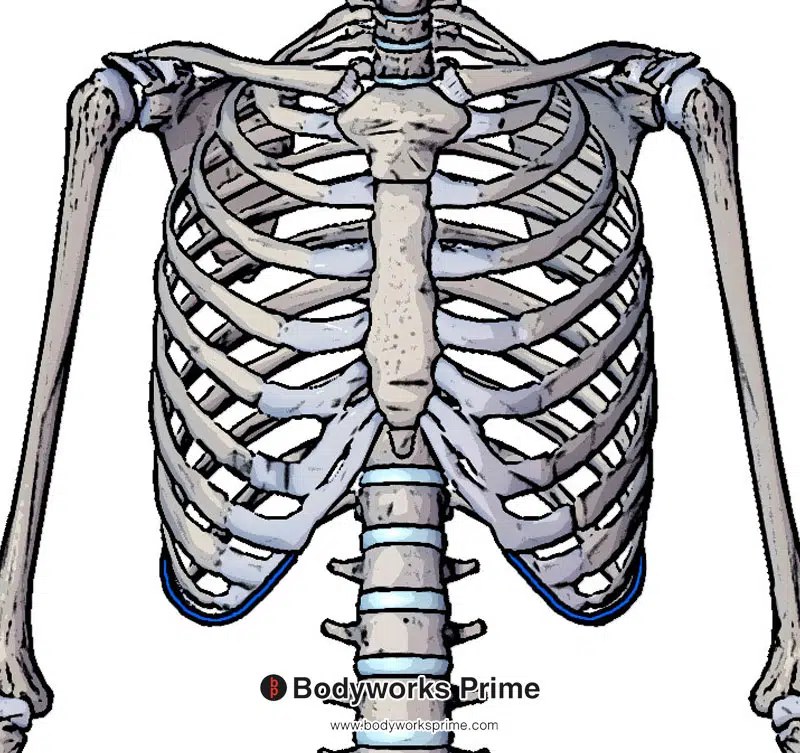
Pictured here we can see the continuation of the insertion on the tenth rib and you can now also see the insertion connecting to the adjacent costal cartilages (highlighted in blue).
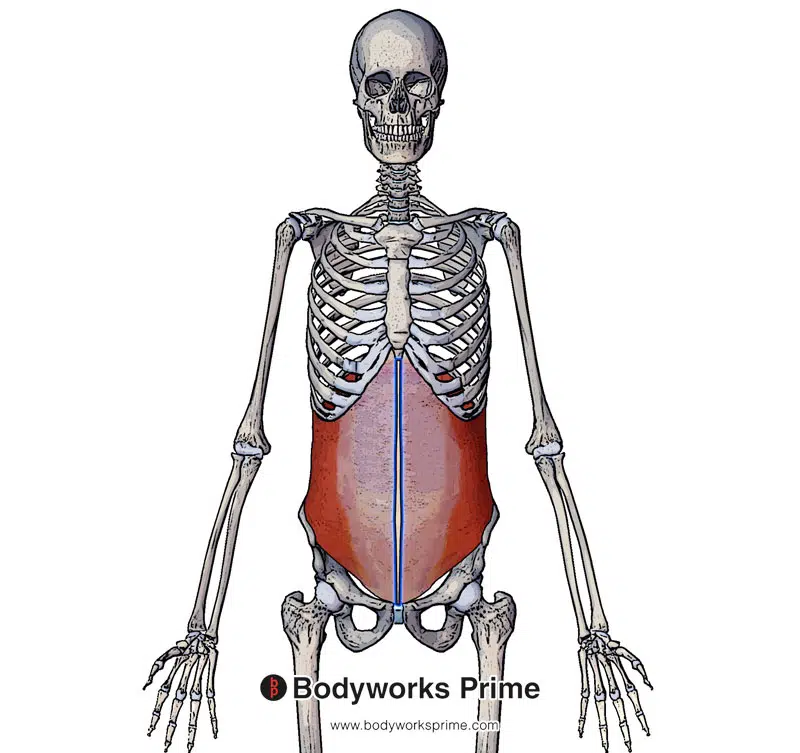
Pictured here we can see an insertion of the internal oblique muscle on the linea alba highlighted in blue. The linea alba is a tendinous, fibrous line that runs vertically down the middle of the abdomen.
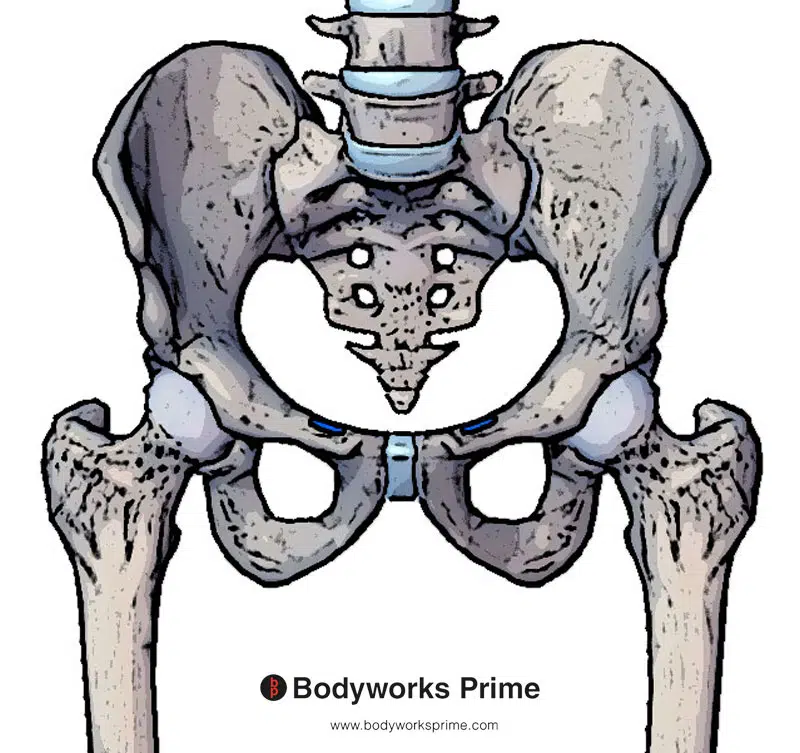
Pictured here we can see an insertion of the internal oblique muscle (highlighted in blue) on the pectineal line.
Actions
When acting with the external oblique, the internal oblique is able to cause flexion, rotation and lateral flexion of the vertebral column. These movements are dependant on if just one side contracts (unilateral contraction) or if both sides contract together (bilateral contraction). Unilateral contraction will result in lateral flexion and rotation of the torso. Bilateral contraction will result in flexion of the torso in an anterior direction. The internal oblique can also work together with other abdominal muscles to increase intrabdominal pressure [7] [8].
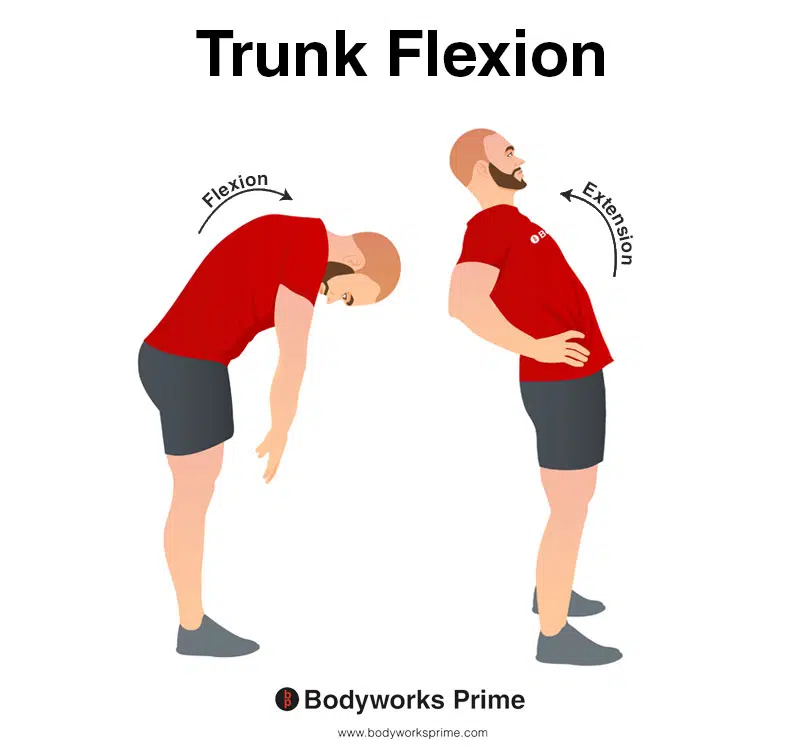
This image shows an example of trunk flexion, which involves bending the torso forwards. The opposite of trunk flexion is trunk extension. Bilateral contraction of the internal oblique contributes to trunk flexion.
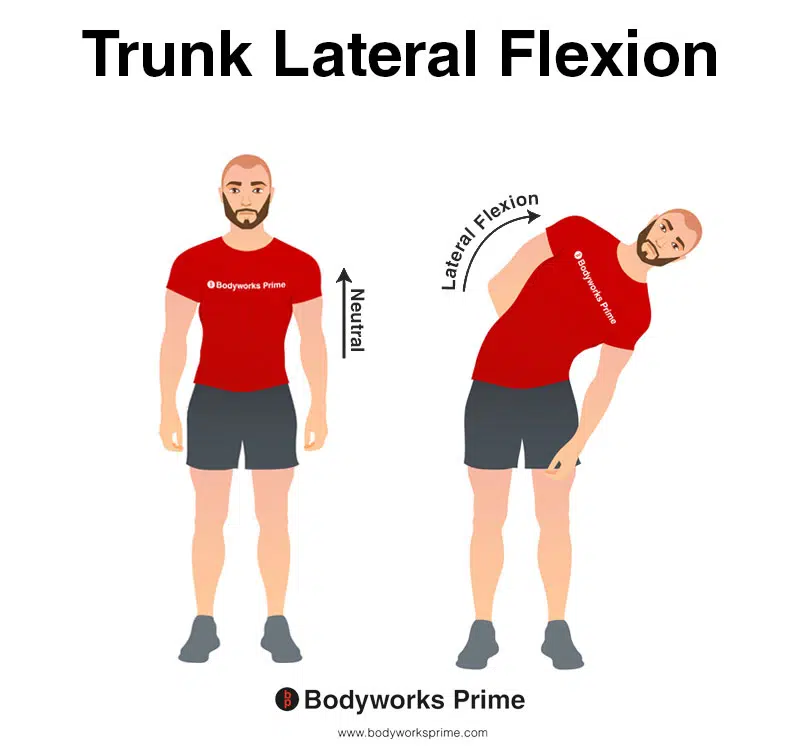
This image demonstrates trunk lateral flexion, which involves bending the torso to the side. Unilateral contraction of the internal oblique contributes to trunk lateral flexion.
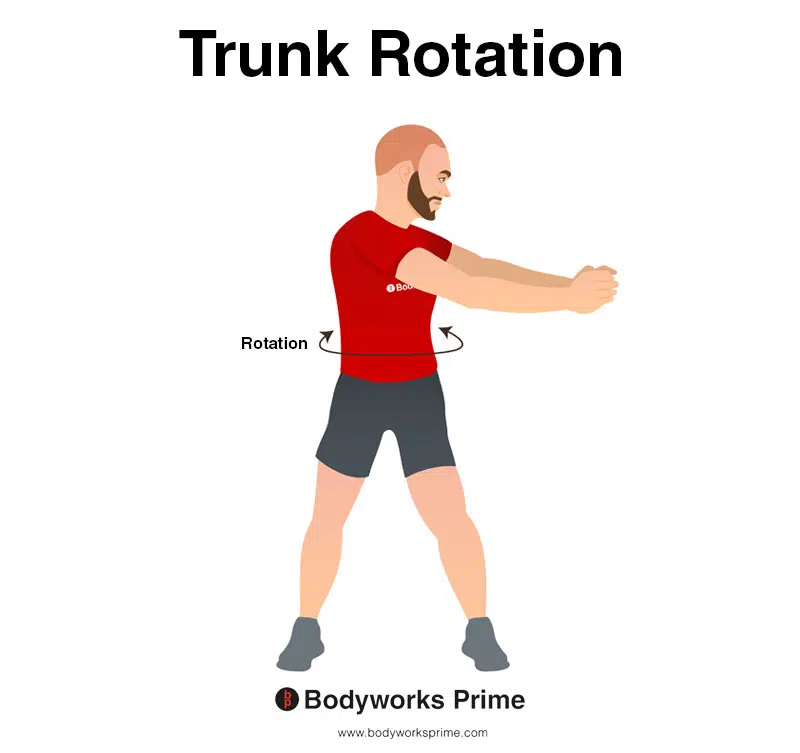
This image demonstrates trunk rotation, which involves twisting the waist/torso to the side. Unilateral contraction of the internal oblique contributes to trunk rotation.
Innervation
The internal oblique muscle is innervated by the anterior rami of intercostal nerves (T7-T1), subcostal nerve (T12), iliohypogastric nerve (L1) and the ilioinguinal nerve (L1) [9] [10].
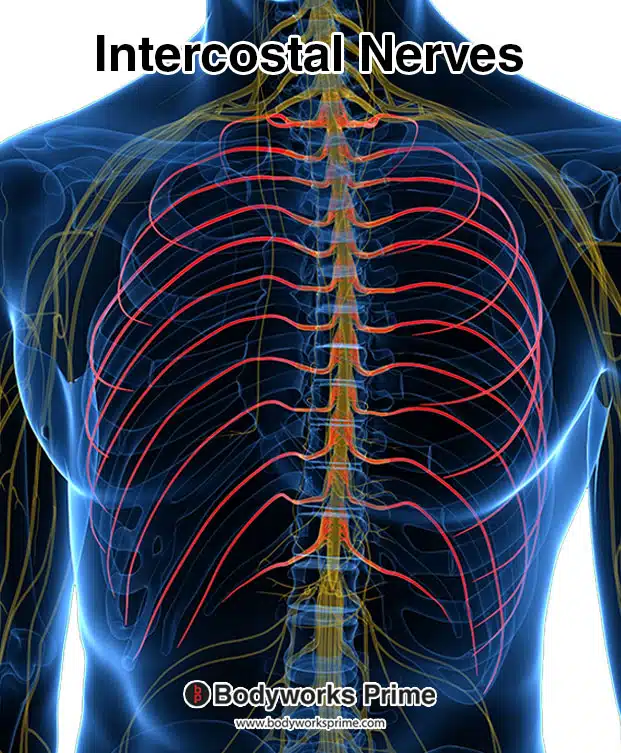
Here we can see the intercostal nerves highlighted in red. These nerves are an innervation of the internal oblique muscle.
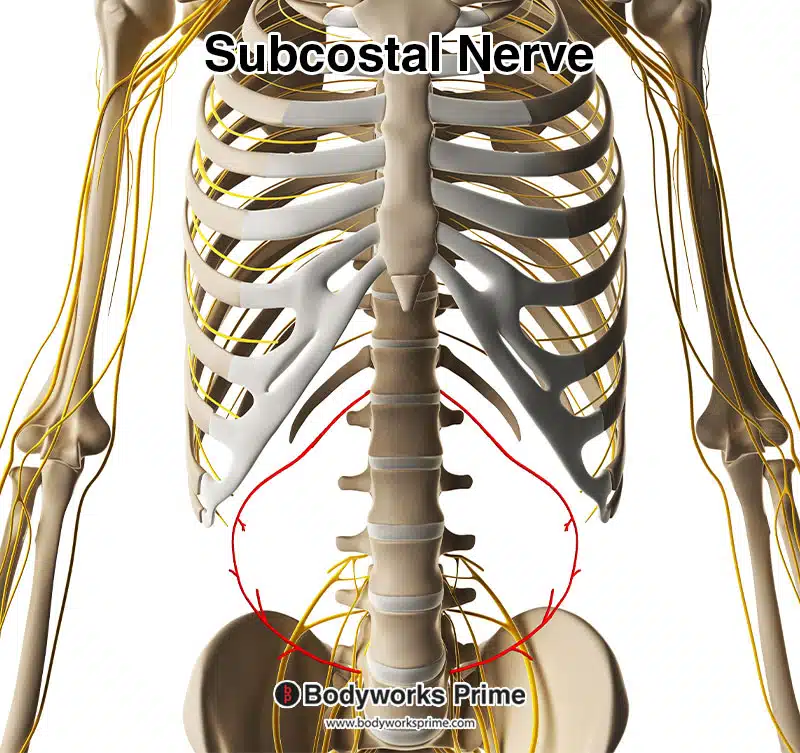
Here we can see the subcostal nerve highlighted in red. The subcostal nerve innervates the internal oblique muscle.
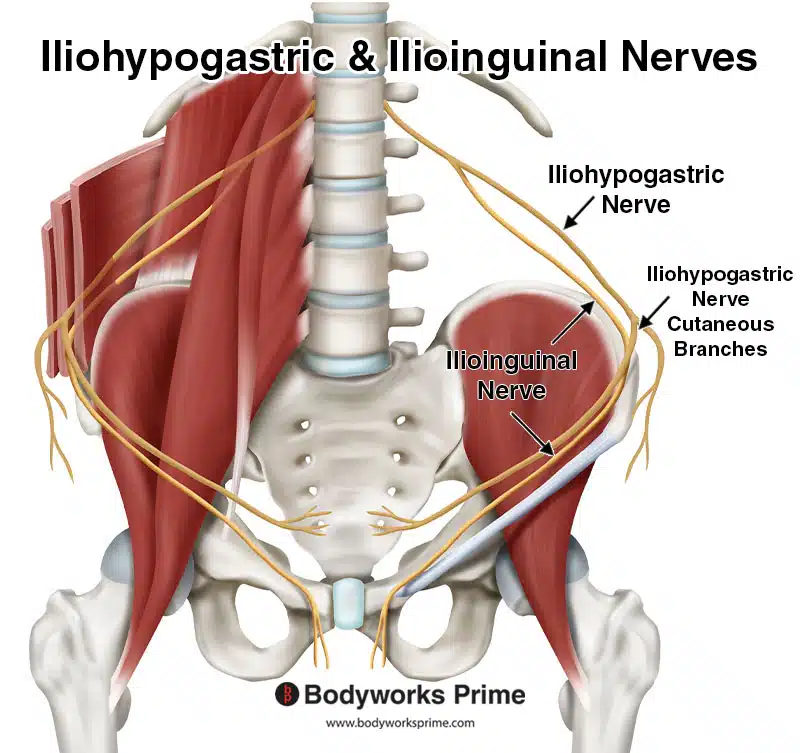
Here we can see the iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves labelled. These nerves innervate the internal oblique muscle. The iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves originate from the lumbar plexus, with both nerves arising primarily from the anterior rami of the first lumbar nerve (L1). Sometimes, the iliohypogastric nerve also receives contributions from the twelfth thoracic nerve (T12). The iliohypogastric nerve has two branches, the lateral cutaneous branch and the anterior cutaneous branch. The anterior branch in this picture is the one going around to the front of the body.
Blood Supply
Blood is supplied to the internal oblique muscle via the lower posterior intercostal arteries and subcostal arteries, superior and inferior epigastric arteries, superficial and deep circumflex arteries, and the posterior lumbar arteries [11] [12].
Want some flashcards to help you remember this information? Then click the link below:
Internal Oblique Flashcards
Support Bodyworks Prime
Running a website and YouTube channel can be expensive. Your donation helps support the creation of more content for my website and YouTube channel. All donation proceeds go towards covering expenses only. Every contribution, big or small, makes a difference!
References
| ↑1, ↑4, ↑7 | Flynn W, Vickerton P. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Abdominal Wall. [Updated 2021 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551649/ |
|---|---|
| ↑2, ↑5, ↑9, ↑11 | Varacallo M, Scharbach S, Al-Dhahir MA. Anatomy, Anterolateral Abdominal Wall Muscles. [Updated 2021 Jul 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470334/ |
| ↑3, ↑6, ↑8 | Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2017 |
| ↑10, ↑12 | Seeras K, Qasawa RN, Ju R, et al. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Anterolateral Abdominal Wall. [Updated 2021 Jul 26]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK525975/ |