| Origin | Inner lip of iliac crest Iliolumbar ligament |
| Insertion | Twelfth rib Transverse processes vertebra L1-L4 |
| Action | Assists with inspiration by bracing the twelfth rib Assists with stabilisation of spine and pelvis Bilateral contraction: Assists with extension of the trunk Unilateral contraction: Assists with lateral flexion of the trunk |
| Nerve | 12th thoracic intercostal nerve Iliohypogastric nerve Ilioinguinal nerve |
| Artery | Lumbar arteries A lumbar branch of the iliolumbar artery |
Location & Overview
The quadratus lumborum muscle, abbreviated as the ‘QL muscle’, is located deep within the lower back musculature towards the posterior of the body. It is classified as a muscle of the posterior abdominal wall and is located dorsally to the iliopsoas muscle. The QL muscle is quadrangular in shape, as reflected by its Latin name ‘quadratus’ lumborum, although its shape may sometimes be irregular. It is positioned laterally on either side of the spine [1] [2].
The quadratus lumborum works alongside muscles such as the multifidus and erector spinae muscle group to extend the back and creates an antagonist force to the muscles of the anterolateral abdomen wall. However, the quadratus lumborum’s contractile force during trunk extension is comparitively weak compared to the the multifidus and erector spinae muscle group. Nevertheless, it is still an important muscle for stabilisation of the spine and pelvis and additionally assists with inspiration by bracing the twelfth rib [3] [4].
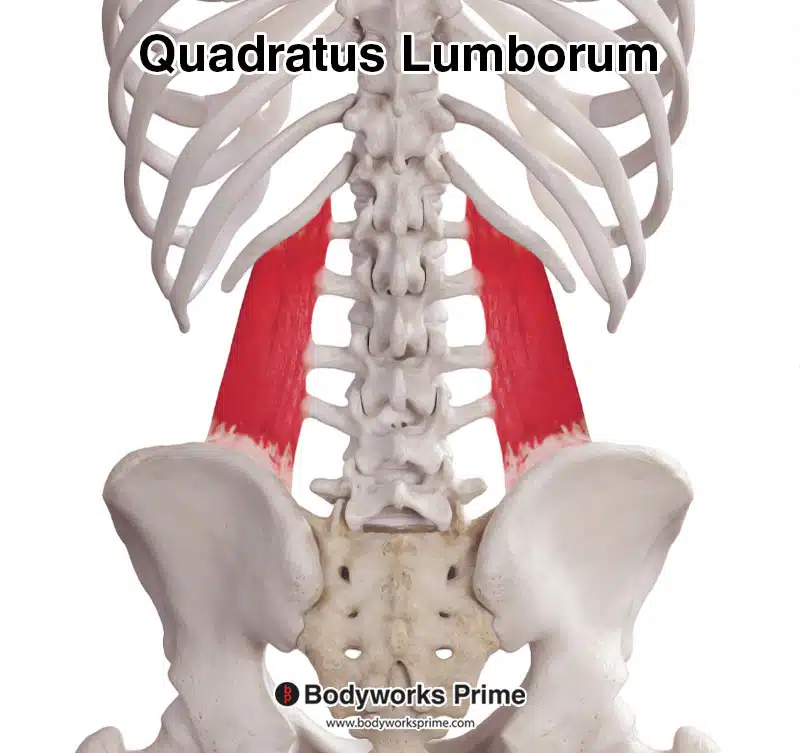
Pictured here we can see the quadratus lumborum muscle from a posterior view.
Origin & Insertion
The quadratus lumborum muscle originates on the inner lip of the iliac crest and iliolumbar ligament. The iliolumbar ligament is a strong ligament connecting the end of the transverse process of the 5th lumbar vertebra (L5) to the posterior and inner lip of the iliac crest (example in the pictures below). The quadratus lumborum inserts onto the internal surface and inferior border of the 12th rib and the transverse processes of vertebra L1 to L4 [5].
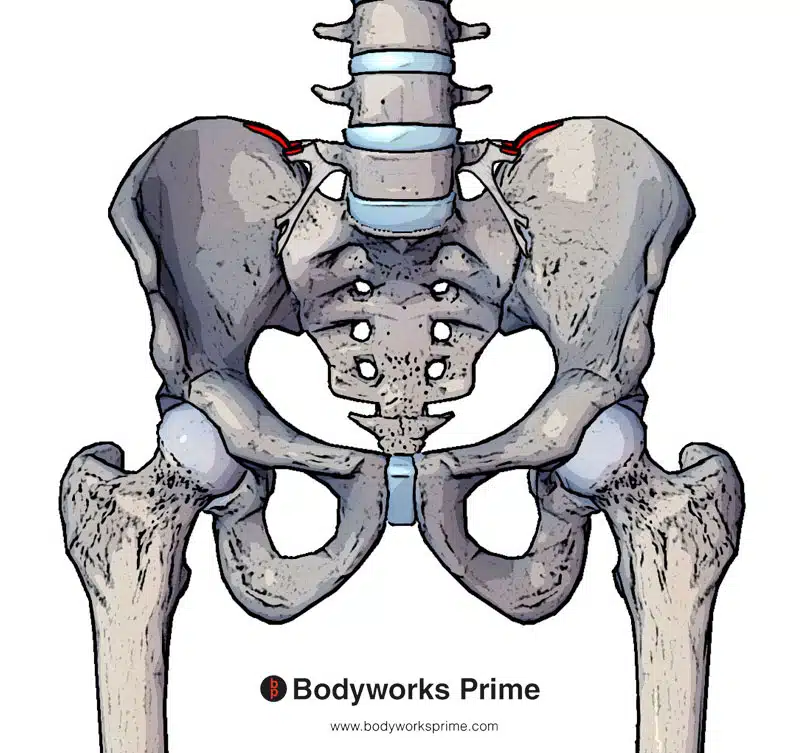
Pictured here we can see the origin points of the quadratus lumborum highlighted in red. The origin points are on the inner lip of iliac crest and the iliolumbar ligament.
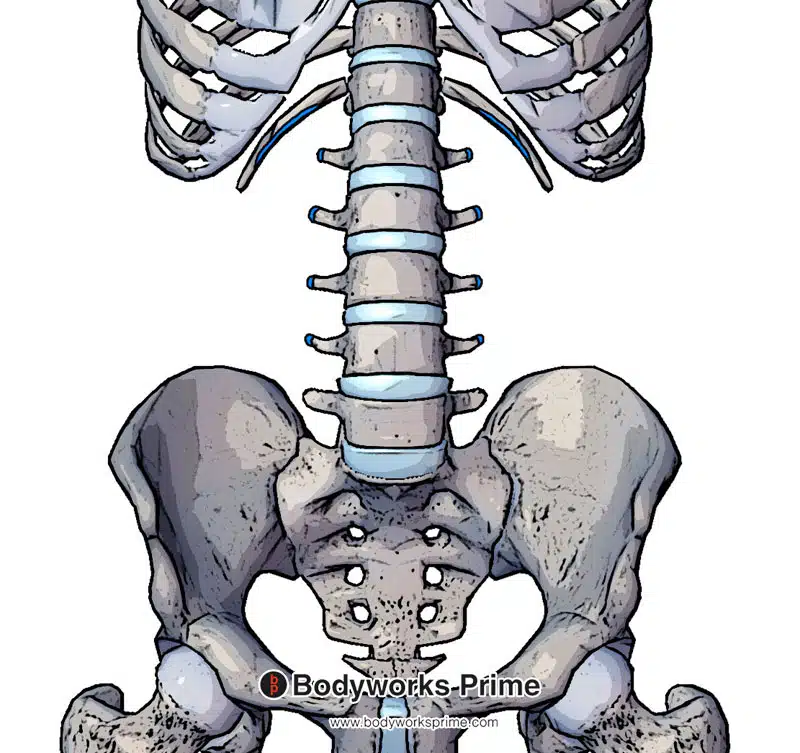
Pictured here we can see the insertion points of the quadratus lumborum highlighted in blue. These insertion points are the 12th rib and the transverse processes of vertebra L1-L4.
Actions
The contraction of both sides of the quadratus lumborum muscle (bilateral contraction) assists in extending the trunk. On the other hand, the contraction of just one side of the muscle (unilateral contraction) helps in lateral flexion of the trunk [6]. The quadratus lumborum can also assist with inspiration (breathing in). It is thought the quadratus lumborum is primarily designed as a respiratory muscle by bracing or anchoring the 12th rib allowing for a stable base for the diaphragm [7].
Compared to other muscles, such as the erector spinae, the quadratus lumborum produces comparatively weaker forces when it comes to extending and laterally flexing the trunk. For instance, the quadratus lumborum can generate only up to 10% of the force that the erector spinae produces during these movements [8] [9]. Even the compression forces produced by the quadratus lumborum are comparatively weak compared to the erector spinae and multifidus muscles. Therefore, it does not play a significant role in stabilization of the lumbar spine either, though it can contribute somewhat. This is thought to be because of the comparatively small size and limited number of muscle fascicles compared to the erector spinae and multifidus [10].
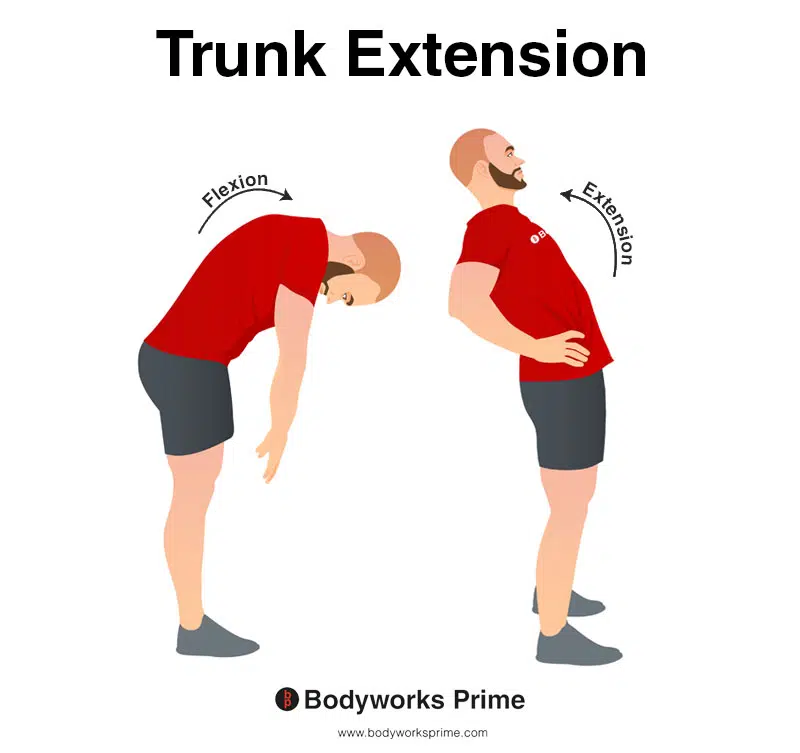
This image demonstrates trunk extension, which involves bending or arching the spine, torso, or back backward. The opposite movement of trunk extension is trunk flexion. A bilateral contraction of the quadratus lumborum can assist with extending the trunk.
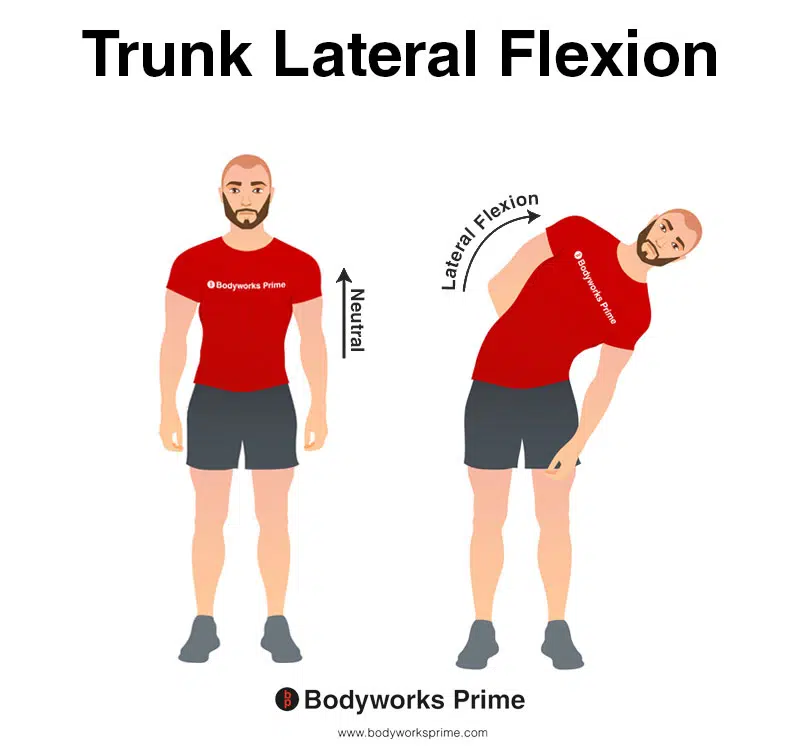
This image demonstrates trunk lateral flexion, which involves bending the torso to the side. Unilateral contraction of the quadratus lumborum can assist with lateral flexion. Additionally, the quadratus lumborum muscle can assist with inspiration by bracing the twelfth rib and contribute to the stabilization of the spine and pelvis (inspiration and stabilization is not depicted in these images).
Innervation
The quadratus lumborum muscle is innervated by the 12th thoracic intercostal nerve, the iliohypogastric nerve, and the ilioinguinal nerve [11] [12].
Blood Supply
Blood is supplied to the quadratus lumborum via the lumbar arteries and a lumbar branch of the iliolumbar artery [13] [14].
Want some flashcards to help you remember this information? Then click the link below:
Quadratus Lumborum Flashcards
Support Bodyworks Prime
Running a website and YouTube channel can be expensive. Your donation helps support the creation of more content for my website and YouTube channel. All donation proceeds go towards covering expenses only. Every contribution, big or small, makes a difference!
References
| ↑1, ↑3, ↑5, ↑6, ↑9, ↑12, ↑14 | Bordoni B, Varacallo M. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Quadratus Lumborum. [Updated 2022 Jul 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535407/ |
|---|---|
| ↑2, ↑4 | Moore KL, Agur AMR, Dalley AF. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; 2017 |
| ↑7, ↑8, ↑10 | Phillips S, Mercer S, Bogduk N. Anatomy and biomechanics of quadratus lumborum. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008 Feb;222(2):151-9. doi: 10.1243/09544119JEIM266. PMID: 18441751. |
| ↑11 | Grzonkowska M, Baumgart M, Badura M, Dombek M, Wiśniewski M, Paruszewska-Achtel M, Szpinda M. Quantitative anatomy of the growing quadratus lumborum in the human foetus. Surg Radiol Anat. 2018 Jan;40(1):91-98. doi: 10.1007/s00276-017-1901-4. Epub 2017 Jul 29. PMID: 28756538; PMCID: PMC5820394. |
| ↑13 | Beveridge TS, Power A, Johnson M, Power NE, Allman BL. The lumbar arteries and veins: Quantification of variable anatomical positioning with application to retroperitoneal surgery. Clin Anat. 2015 Jul;28(5):649-60. doi: 10.1002/ca.22504. Epub 2015 Feb 2. PMID: 25644404 |