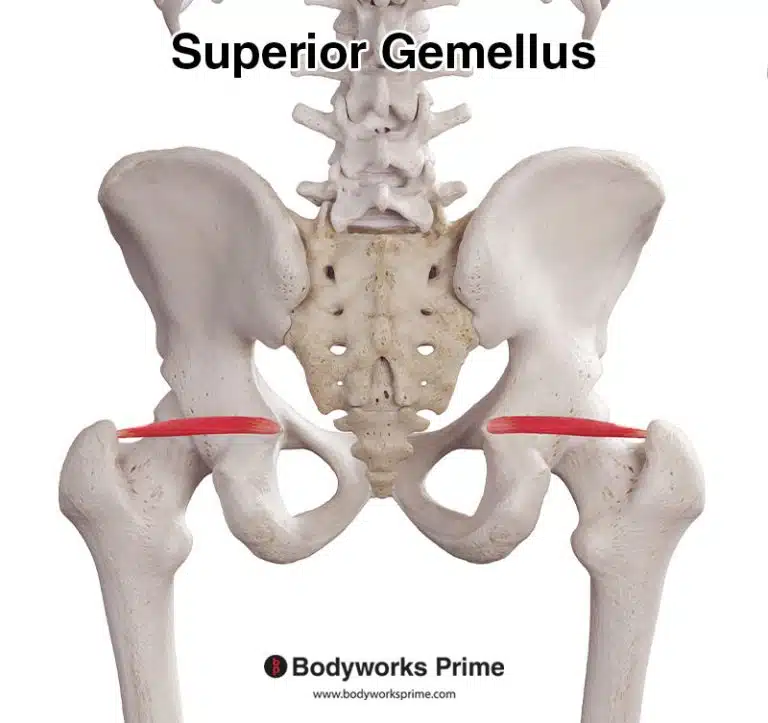
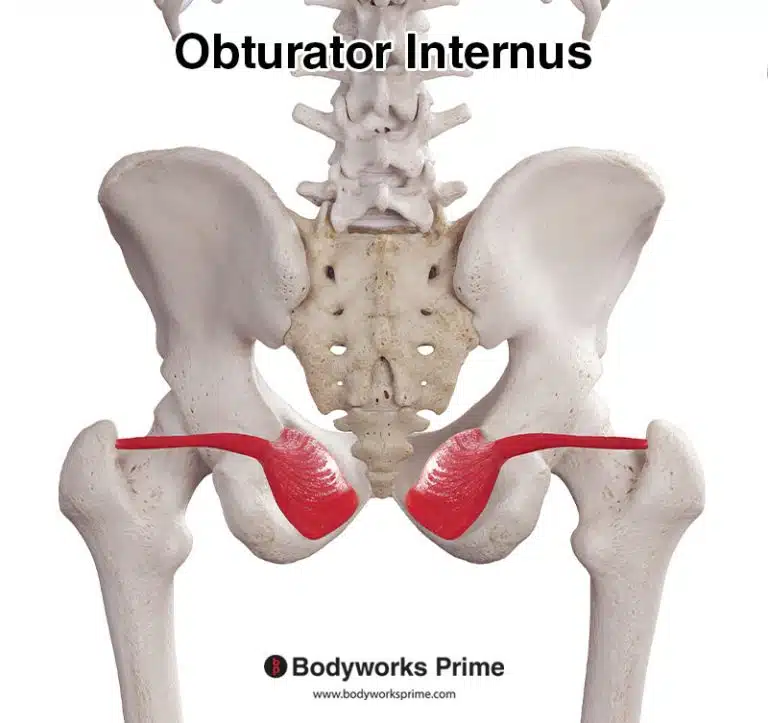
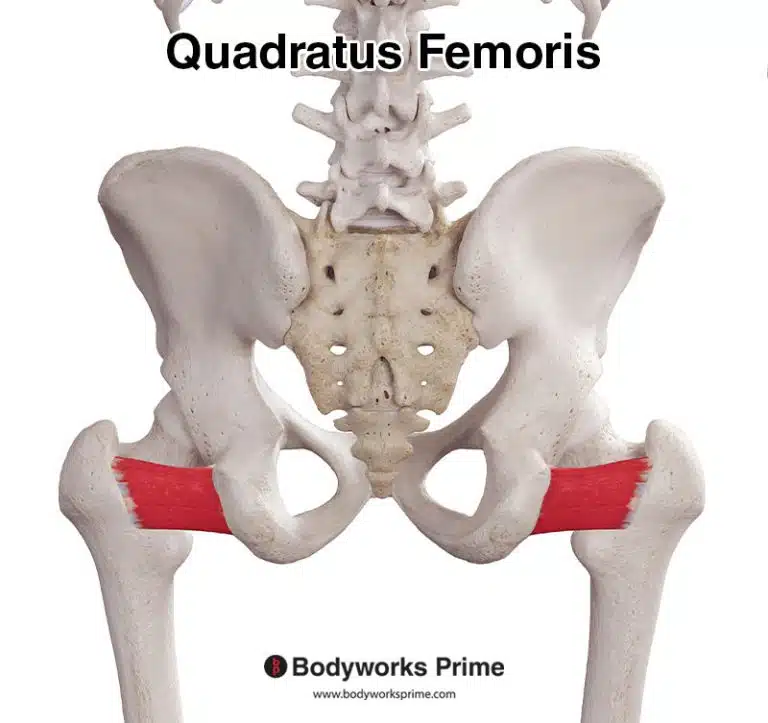
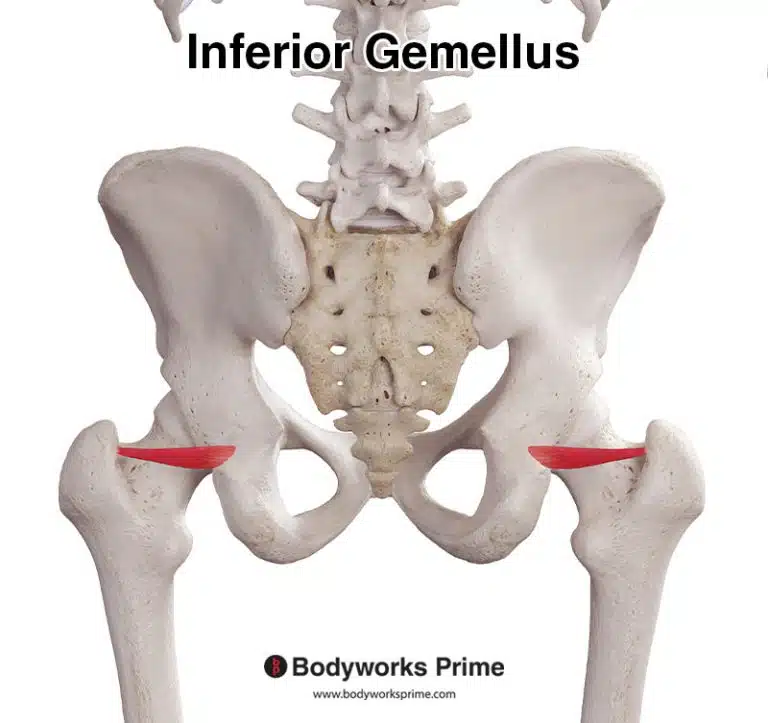
| Origin | Distal & anterior fibula, specifically the lower third or quarter Anterior intermuscular septum Interosseous membrane |
| Insertion | Dorsal aspect of the base of the fifth metatarsal. |
| Action | Dorsiflexion of the foot Eversion of the foot |
| Nerve | Deep fibular nerve (aka deep peroneal nerve), L5 & S1 |
| Artery | Anterior tibial artery Perforating branch of the fibular artery |
Location & Overview
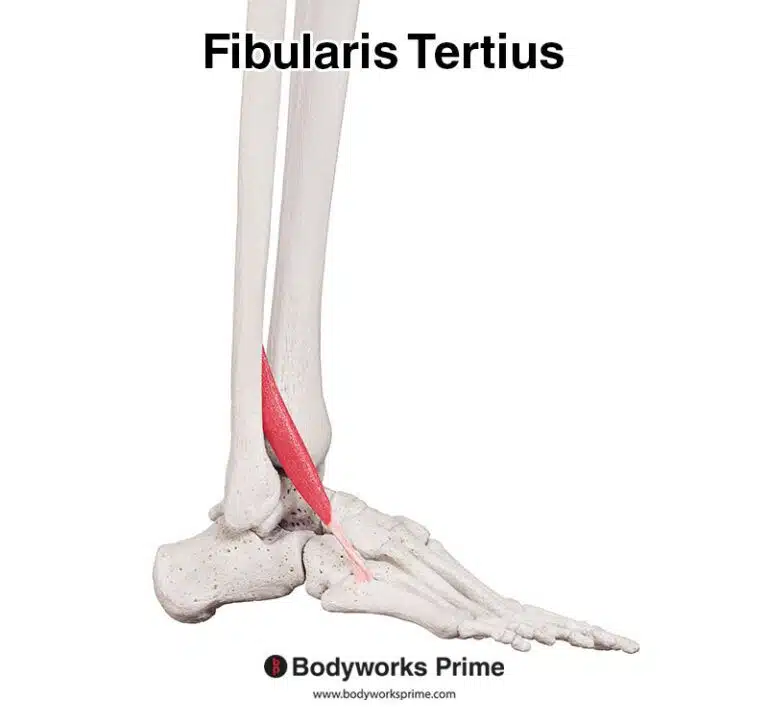
The fibularis tertius, which was previously named the peroneus tertius, is a muscle located on the lateral aspect of the lower leg. This muscle is one of three other fibularis muscles, alongside the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis. This muscle is absent in some individuals. Its tendon courses deep beneath the superior extensor retinaculum and within the inferior extensor retinaculum, it also traverses anterior to the anterior talofibular ligament of the ankle joint. Notably, it often appears to be part of extensor digitorum longus muscle, running directly alongside it until its tendon deviates towards the fifth metatarsal, indicative of these two muscles’ close anatomical relationship [1] [2] [3].
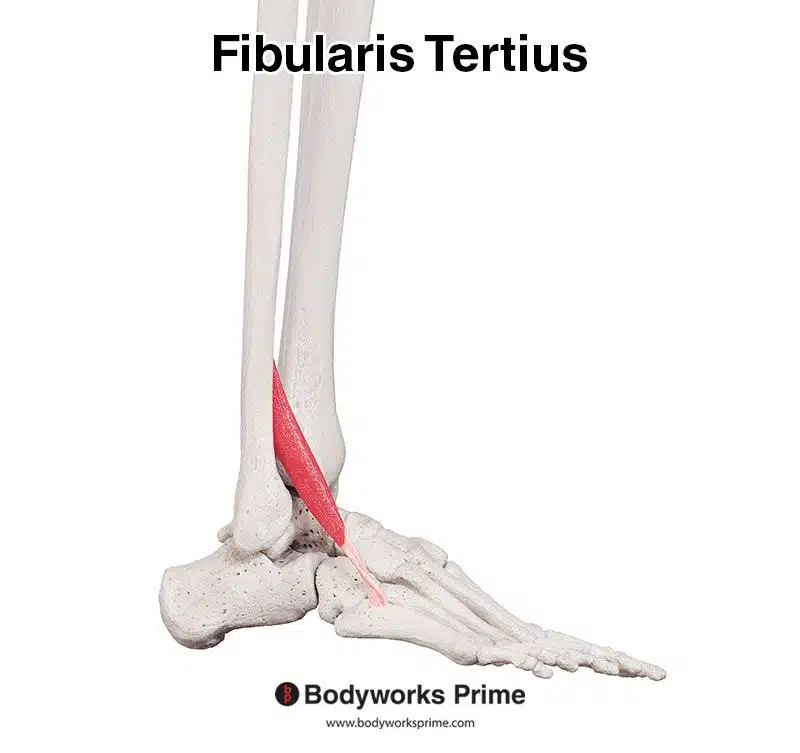
Pictured here, we can see the fibularis tertius muscle seen from a lateral view.
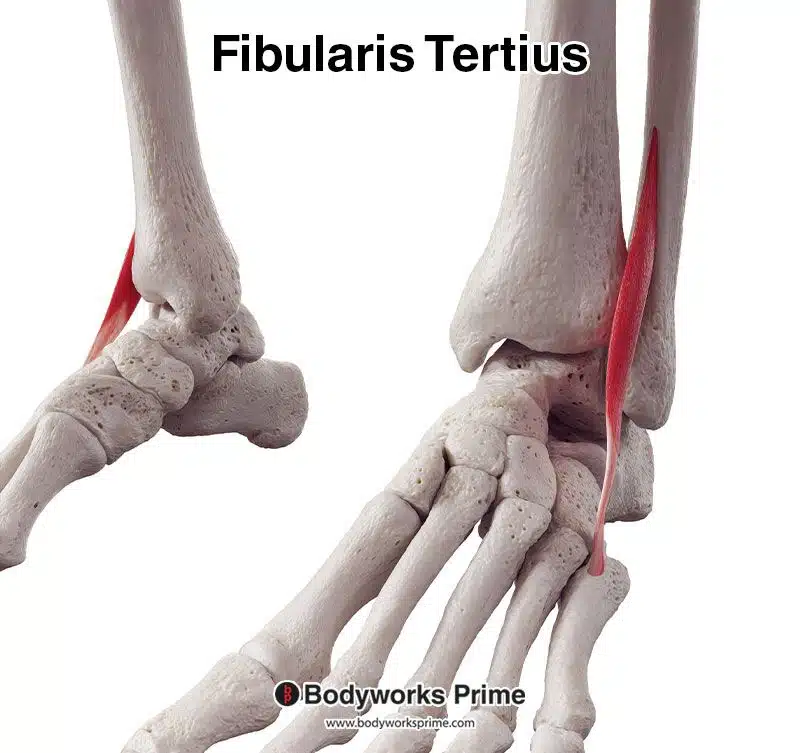
Pictured here, we can see the fibularis tertius muscle seen from an anterolateral view.
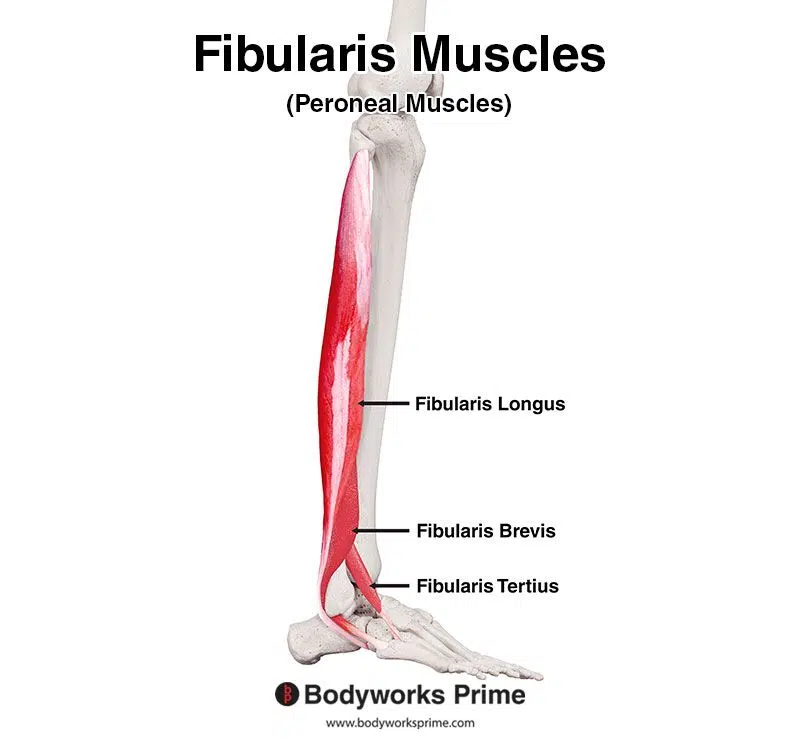
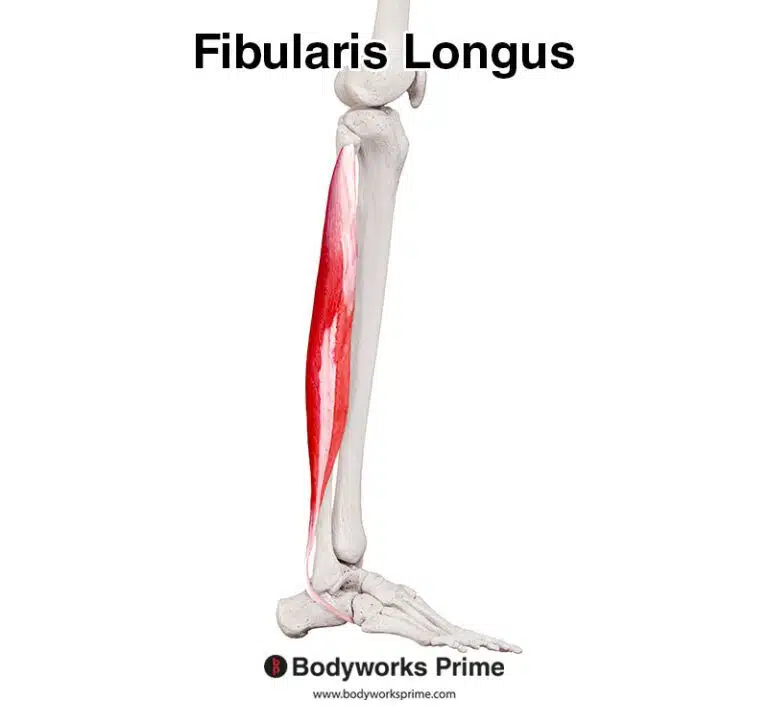
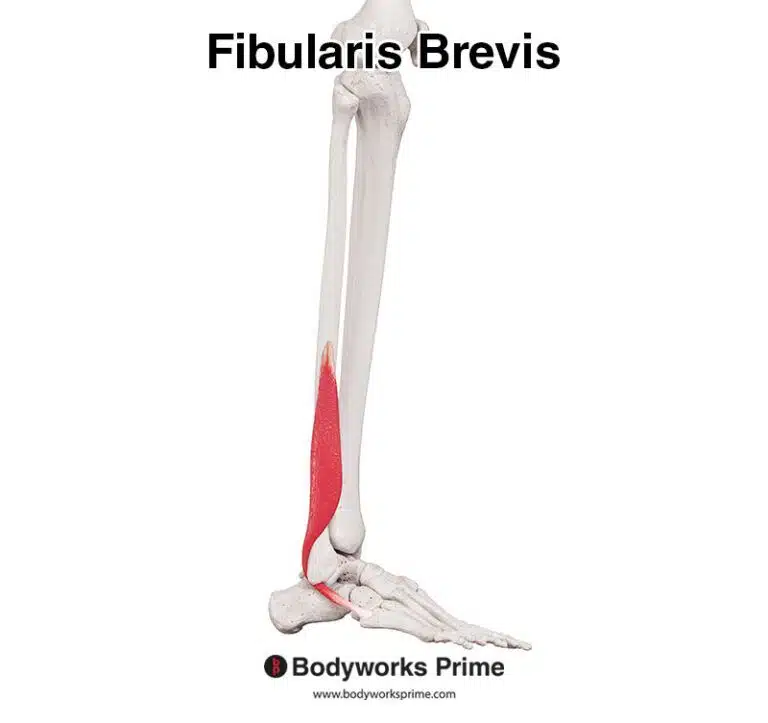
Pictured here, we can see all three of the fibularis muscles: the fibularis longus, fibularis brevis, and fibularis tertius.
Origin & Insertion
The fibularis tertius primarily originates from the distal and anterior portion of the fibula, specifically the lower third or quarter (with individual variances). Further origin points are the anterior intermuscular septum, and the interosseous membrane. The intermuscular septa are fibrous partitions that separate adjacent muscle compartments, providing structural support and helping to organise muscles, nerves, and blood vessels. The interosseous membrane is a fibrous, sheet-like structure that connects the tibia and fibula bones. The fibularis tertius’ origin on the fibula sometimes appears contiguous with the extensor digitorum longus muscle, emphasising their intertwined nature. From its origin, the fibularis tertius crosses the ankle joint and inserts onto the fifth metatarsal, specifically, the dorsal aspect of its base [4] [5] [6].
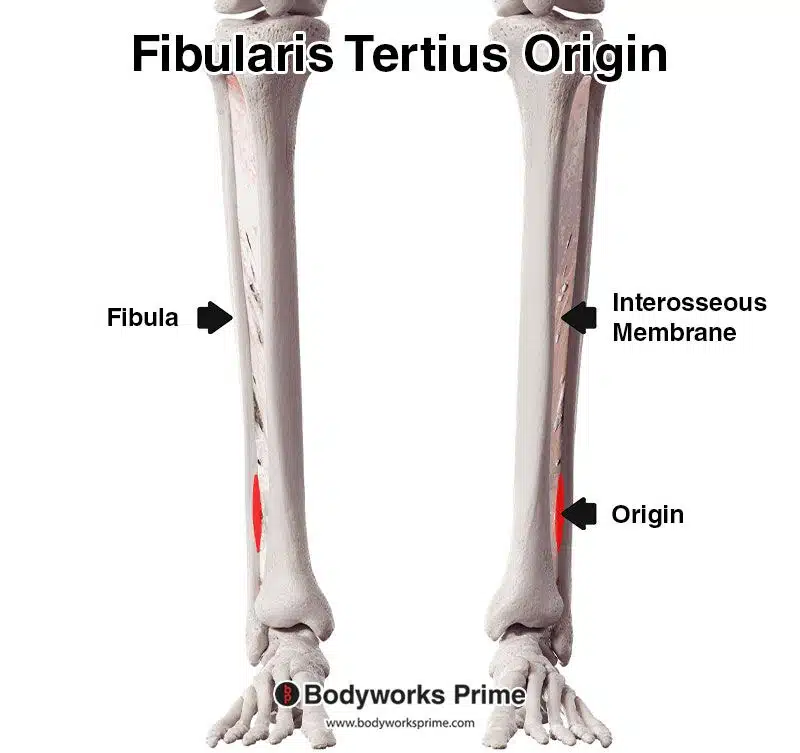
Pictured here, we can see the origin of the fibularis tertius highlighted in red on the lower third of the distal and anterior portion of the fibula as well as on the interosseous membrane.
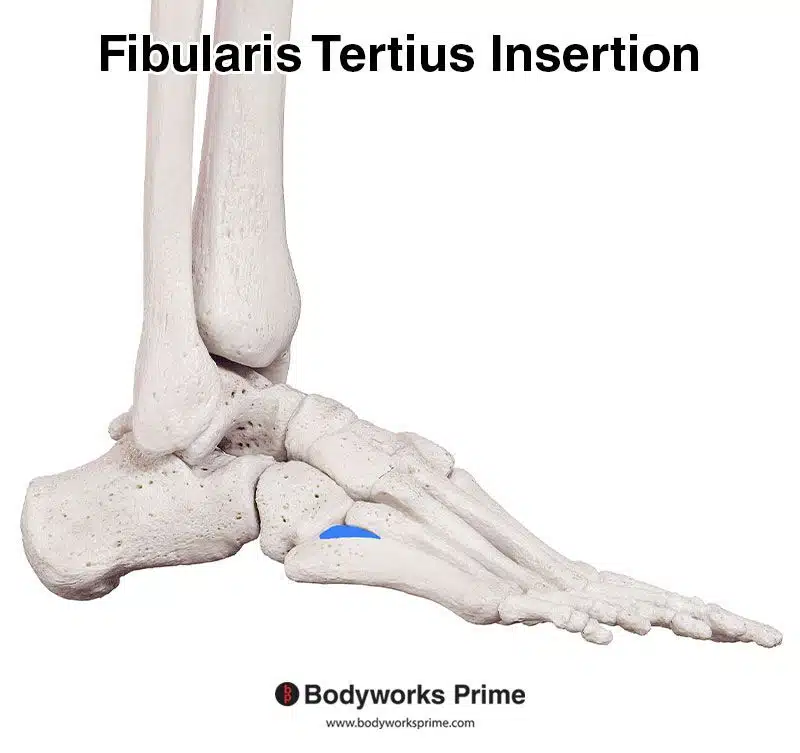
Pictured here, we can see the insertion of the fibularis tertius highlighted in blue on the the dorsal aspect of the base of the fifth metatarsal.
Actions
The fibularis tertius is primarily involved in dorsiflexion of the foot, elevating the foot towards the shin. It also plays a supporting role in the eversion of the foot, aiding in its outward movement. These movements are demonstrated in the images below [7] [8] [9].
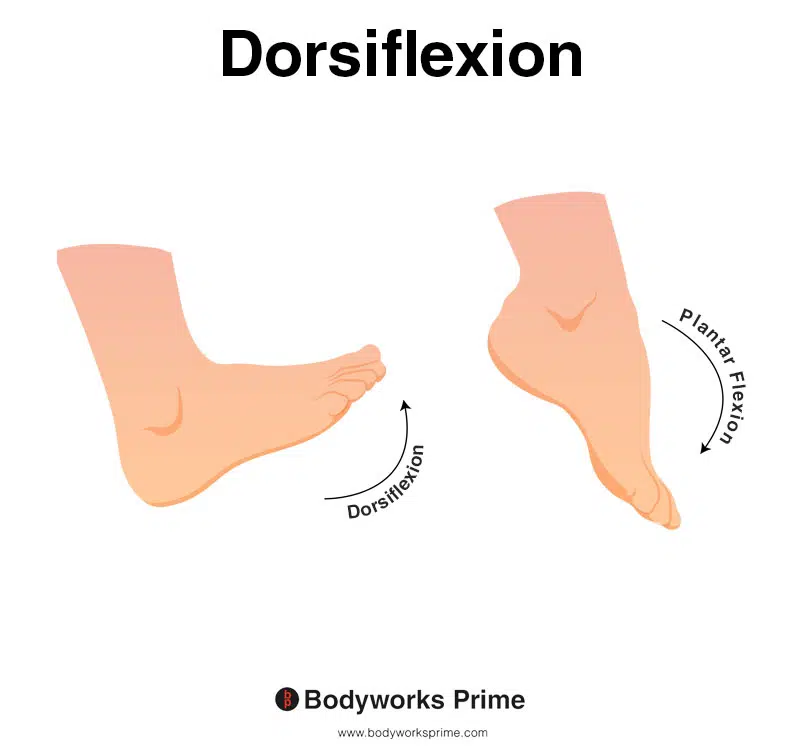
This image shows an example of dorsiflexion of the foot, which involves flexing the ankle joint, thereby lifting the foot upwards and towards the shins. The opposite of dorsiflexion is plantar flexion. The fibularis tertius is primarily involved in dorsiflexion of the foot.
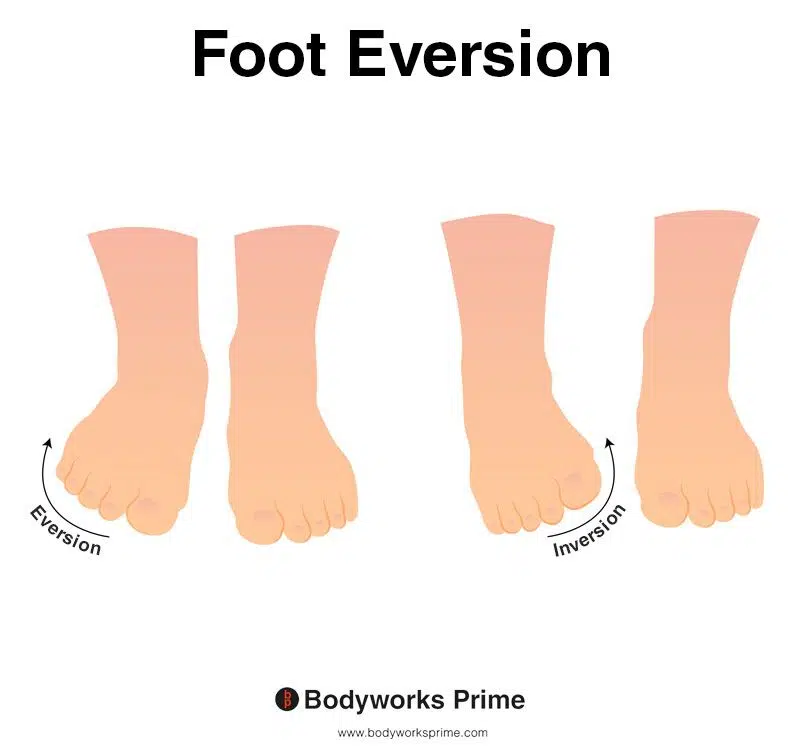
This picture demonstrates foot eversion, which means rotating the foot outwards, causing the sole of the foot to turn away from the body. The opposite of eversion is inversion. The fibularis tertius assists with eversion of the foot.
Innervation
The fibularis tertius is innervated by the deep fibular (peroneal) nerve, with roots from spinal segments L5 and S1. The deep fibular nerve is a terminal division of the common fibular nerve, which is a branch of the sciatic nerve [10] [11] [12].
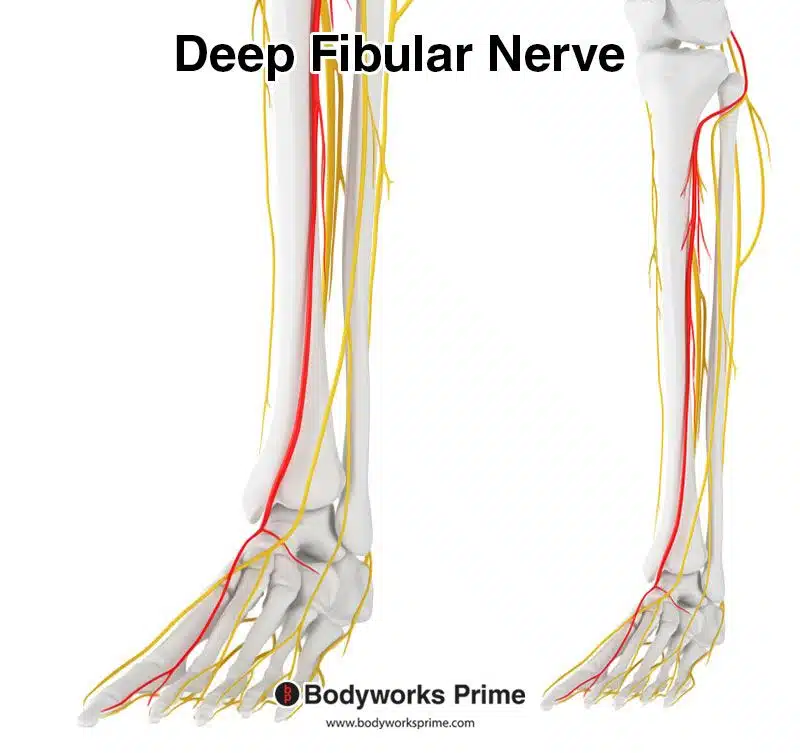
Pictured here, we can see the deep fibular nerve highlighted in red (also known as the deep peroneal nerve). The deep fibular nerve innervates the fibularis tertius from the nerve roots of L5 and S1.
Blood Supply
The fibularis tertius receives blood via the anterior tibial artery and the perforating branch of the fibular artery. The anterior tibial artery is a significant blood vessel that travels down the front of the leg and supplies blood to the muscles there, including the fibularis tertius. Meanwhile, the fibular artery, another major vessel in the leg, runs closer to the outer side of the leg and also sends blood to this muscle through a ‘perforating’ branch, meaning a smaller vessel that extends or passes through from the main artery.
Want some flashcards to help you remember this information? Then click the link below:
Fibularis Tertius Flashcards
Support Bodyworks Prime
Running a website and YouTube channel can be expensive. Your donation helps support the creation of more content for my website and YouTube channel. All donation proceeds go towards covering expenses only. Every contribution, big or small, makes a difference!
References
| ↑1, ↑4, ↑10 | Dalley AF II, Agur AMR. Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 9th ed. Wolters Kluwer Health; 2022. |
|---|---|
| ↑2, ↑5, ↑7, ↑11 | Standring S. (2015). Gray’s Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice, 41st Edn. Amsterdam: Elsevier |
| ↑3, ↑6, ↑8, ↑12 | Palastanga N, Soames RW. Anatomy and Human Movement: Structure and Function (Physiotherapy Essentials), 6th ed. Elsevier; 2011. ISBN-13: 978-0702035531. |
| ↑9 | Gupton M, Munjal A, Kang M. Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb: Fibula. [Updated 2023 May 23]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470591/ |